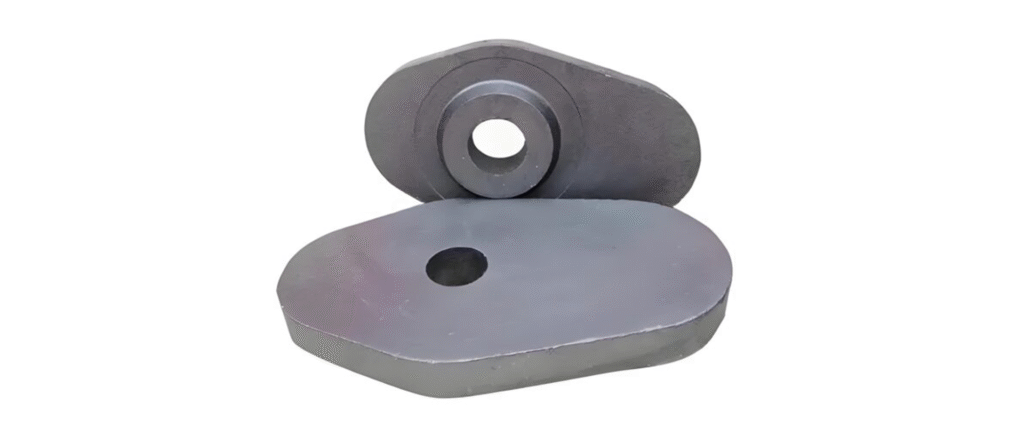
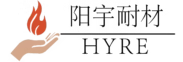Research Background
-
- Longer lifetime of Sliding-Gate is needed
-
- JFE and POSCO are developing reusable outer plate technology
- Research is needed to understand and present cracks in ladle plates
Why are cracks in sliding-gate a concern
- Safety Problem (Steel leakage)
- Clogging (Air penetration)
- Require replacing plate every heat
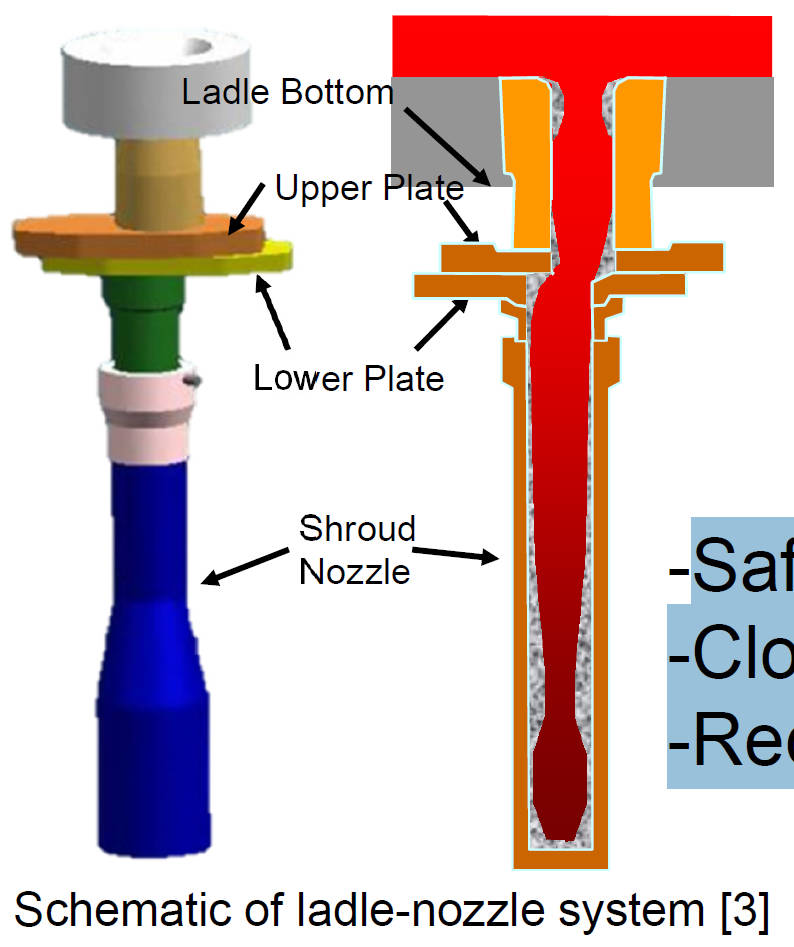
Schematic of Ladle-Nozzle Sliding-Gate System
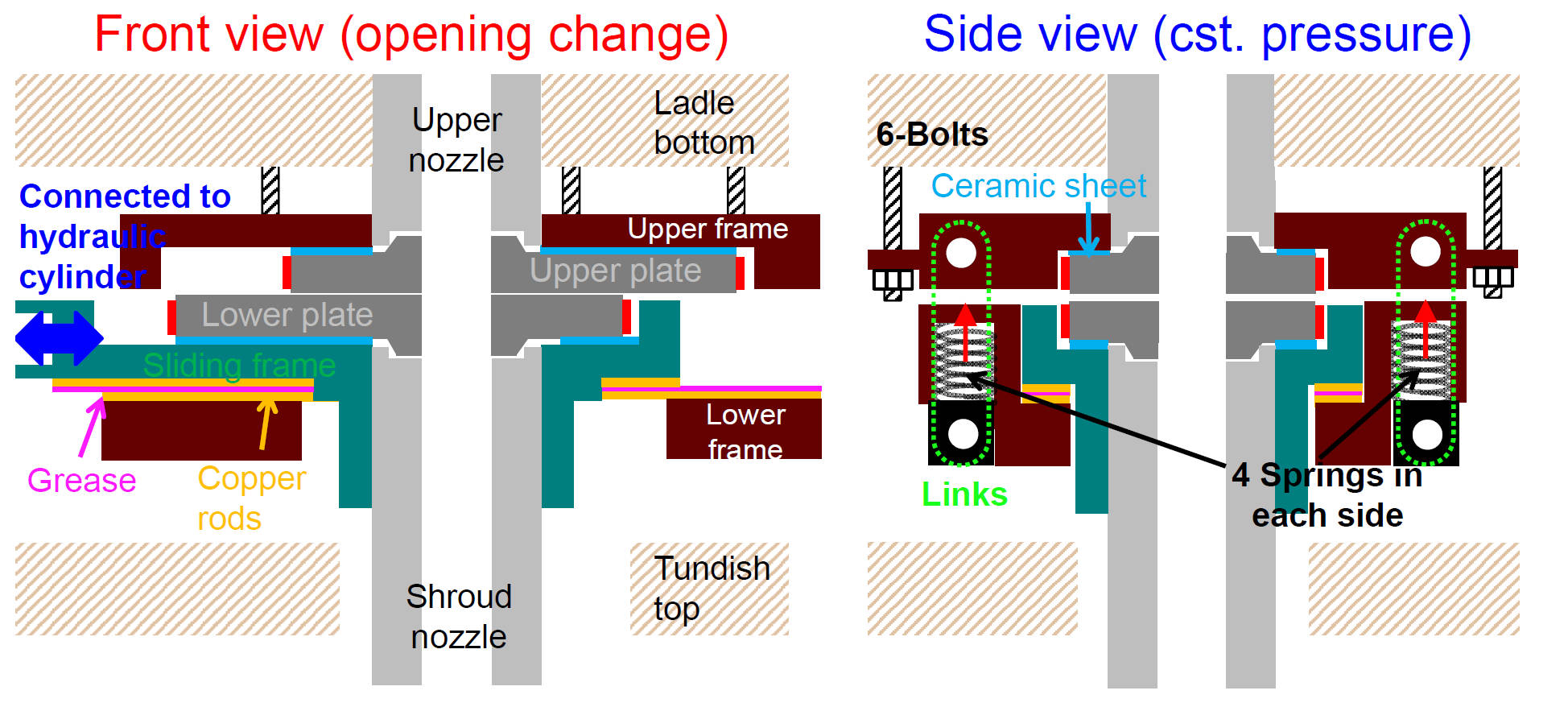
- Lower plate moves horizontally to control the molten steel
flow rate through the nozzle
- Springs generate cassette pressure on the ladle plate
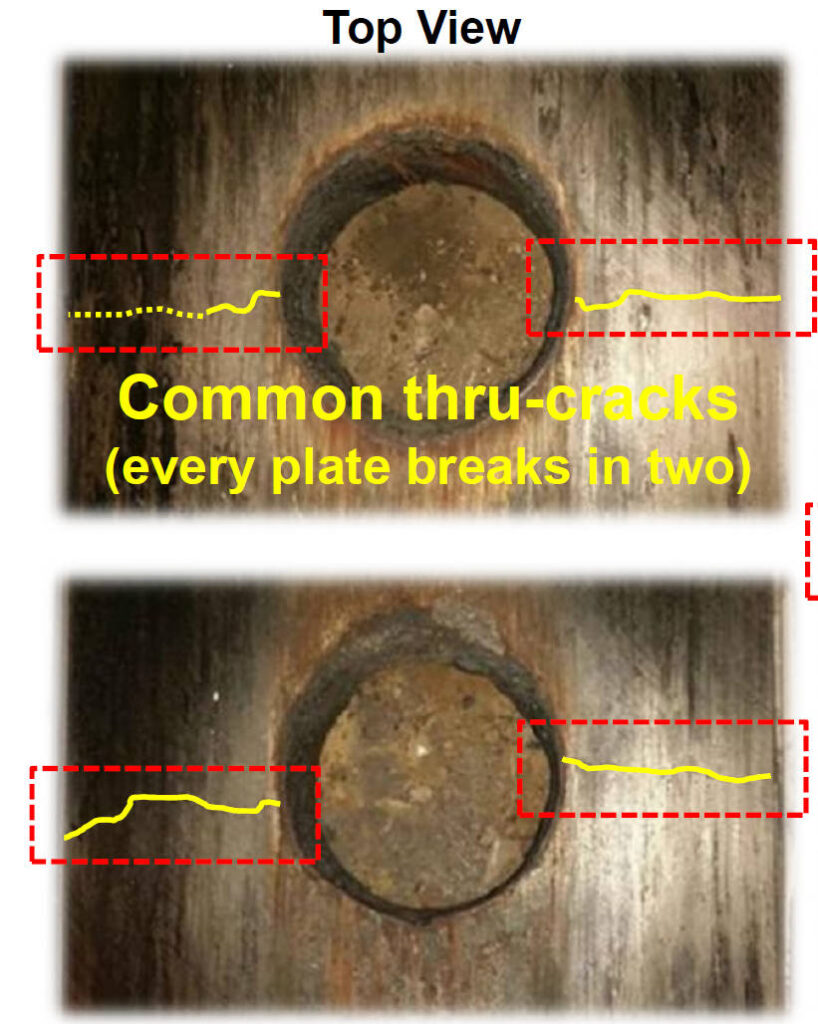
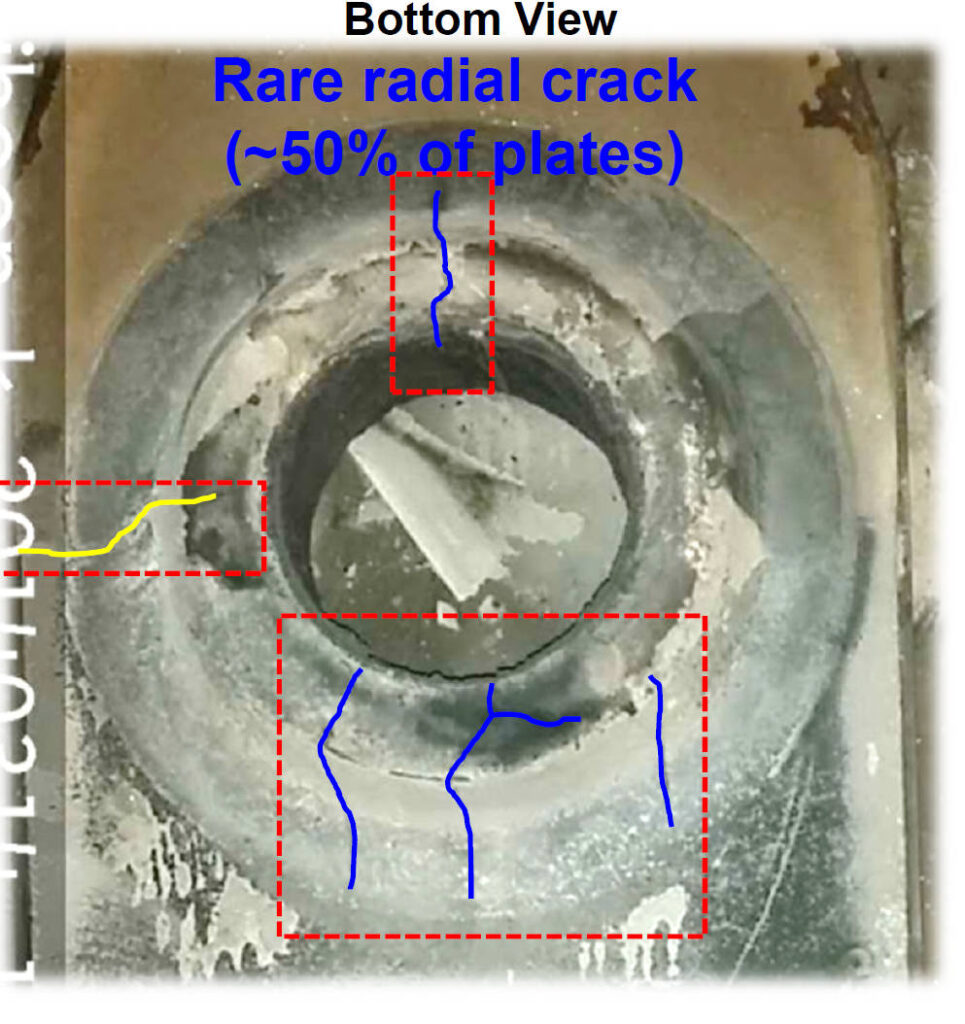
Type of Ladle Plate Cracks
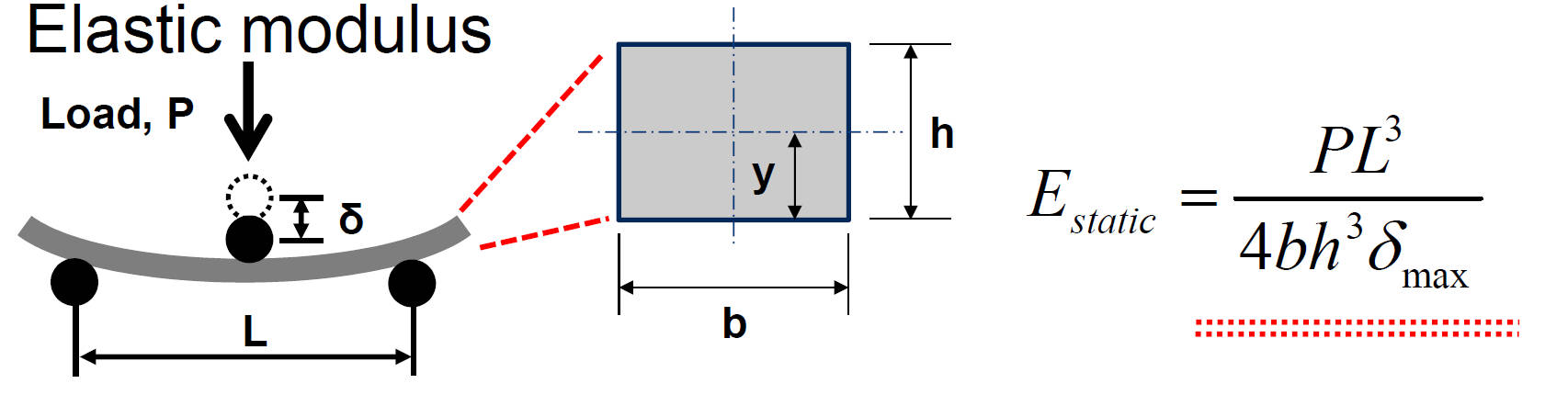
Method of Elastic Modulus Calibration by 3-Point Bending Test
Data vs time from bending test at 1200°C, #1
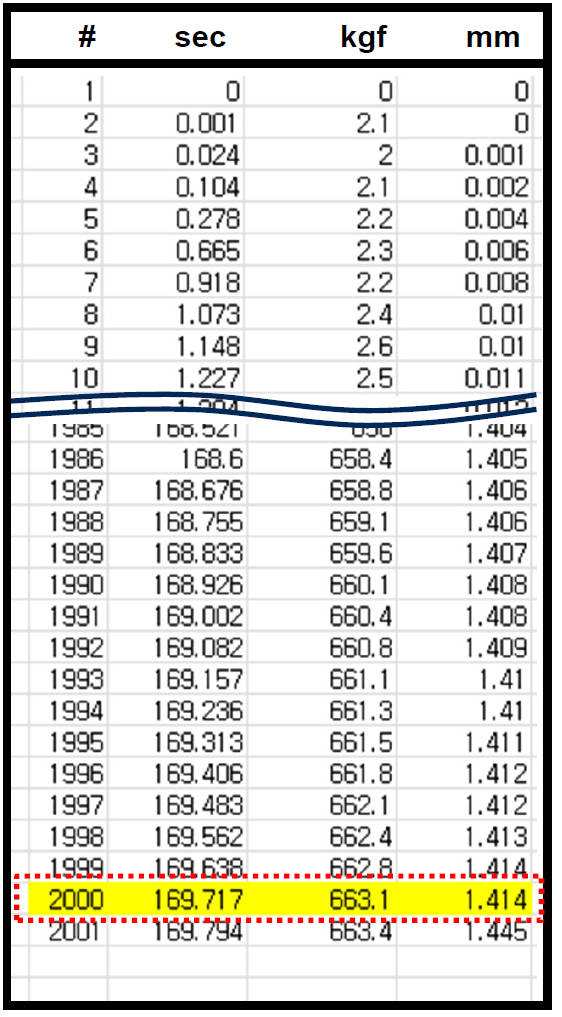
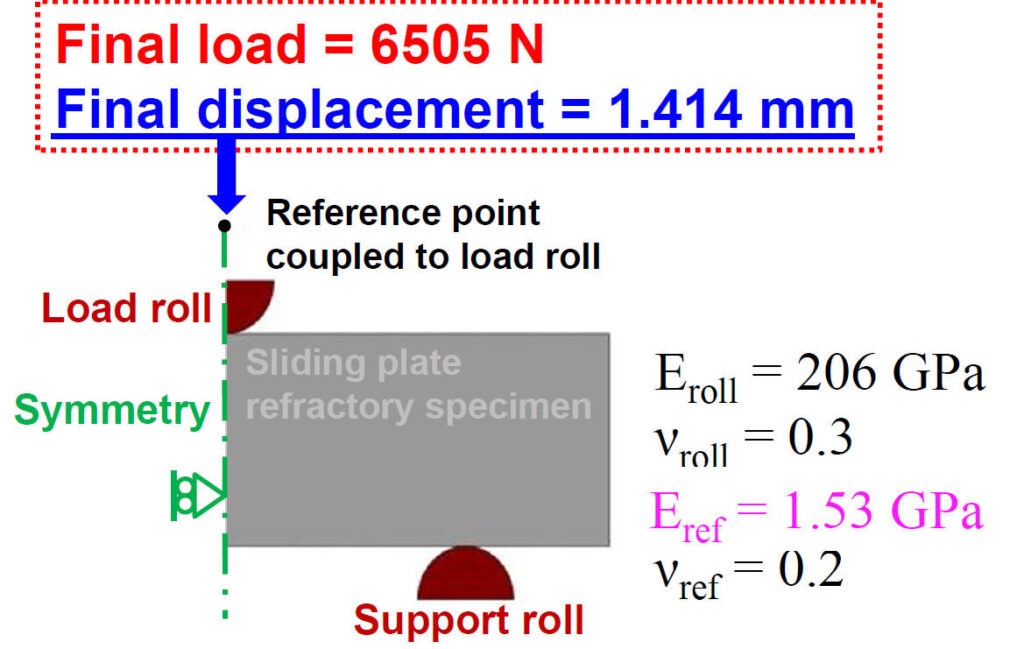
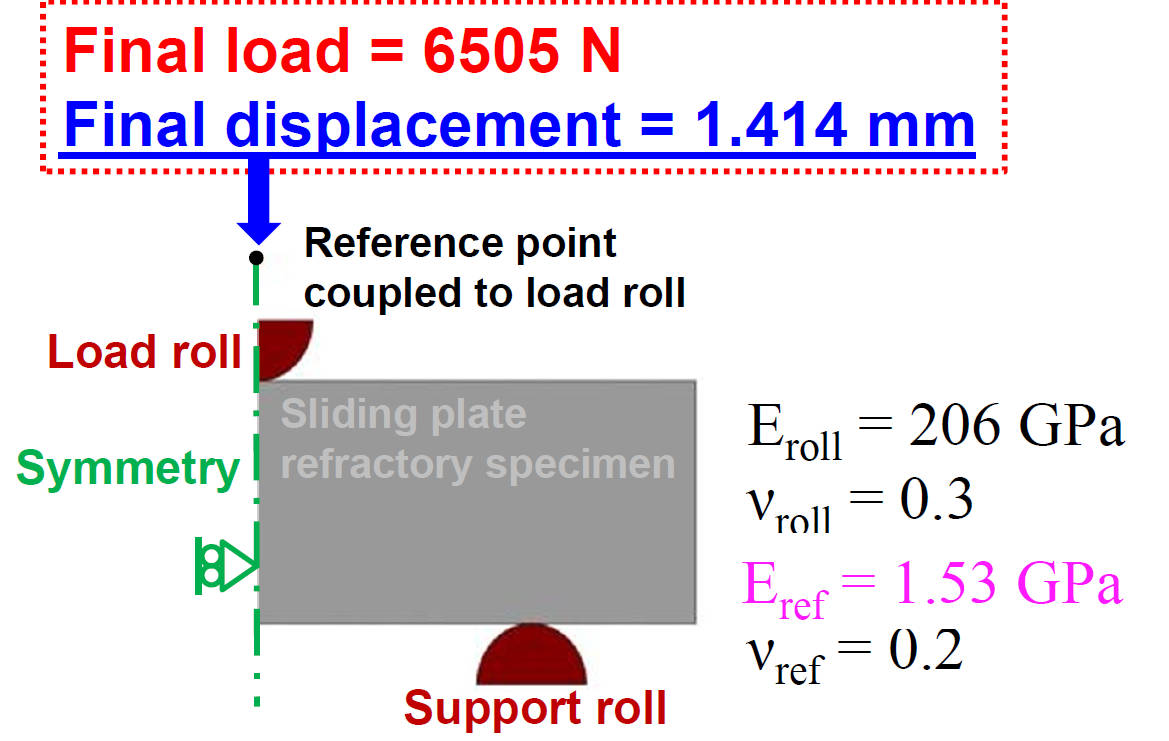
Elastic modulus is adjusted until reaction force on reference point in FEM matches to final load of measurement
2-D Finite Element Model of 3-Point Bending Test
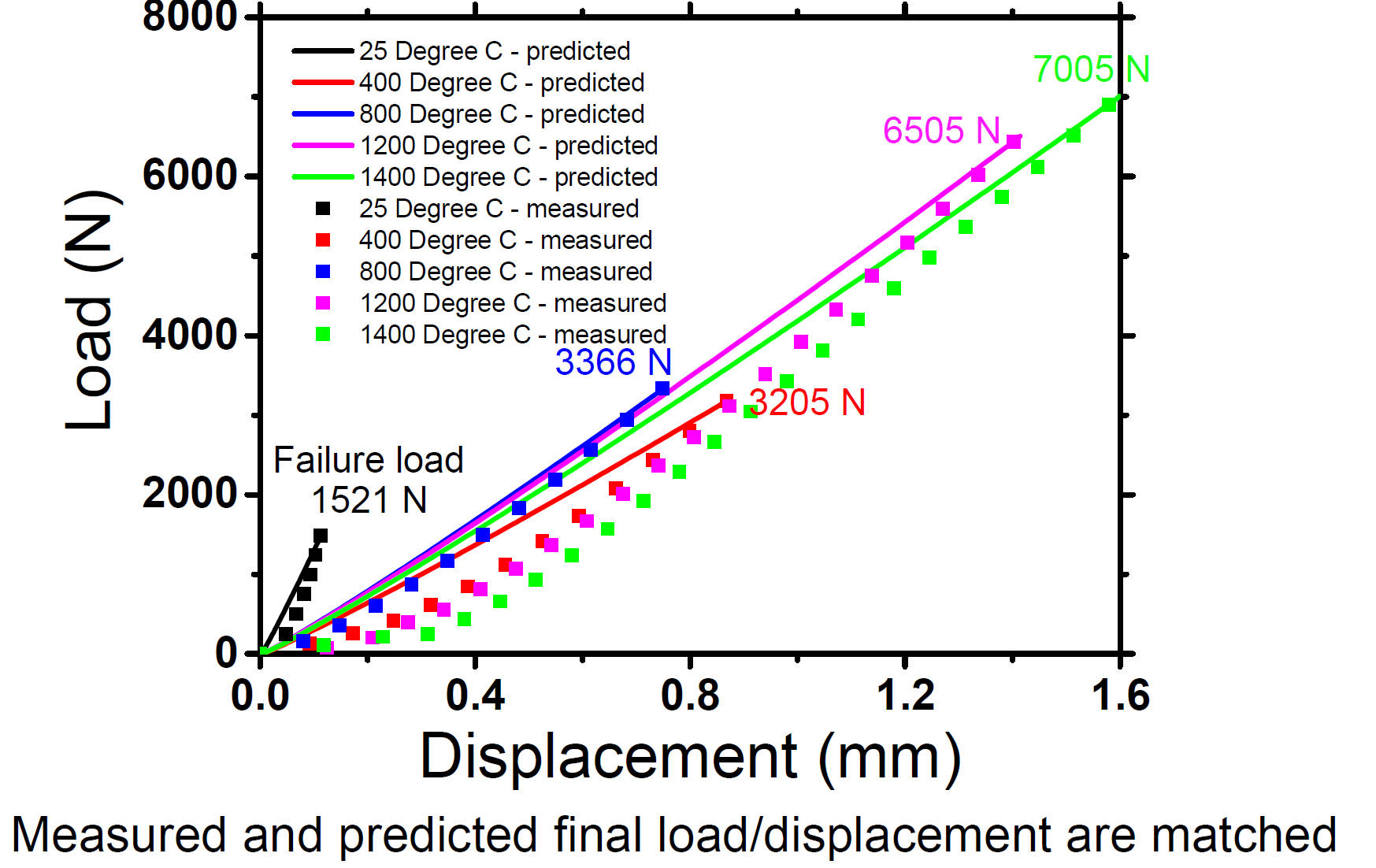
3-Point Bending Test Results at Different Temperatures
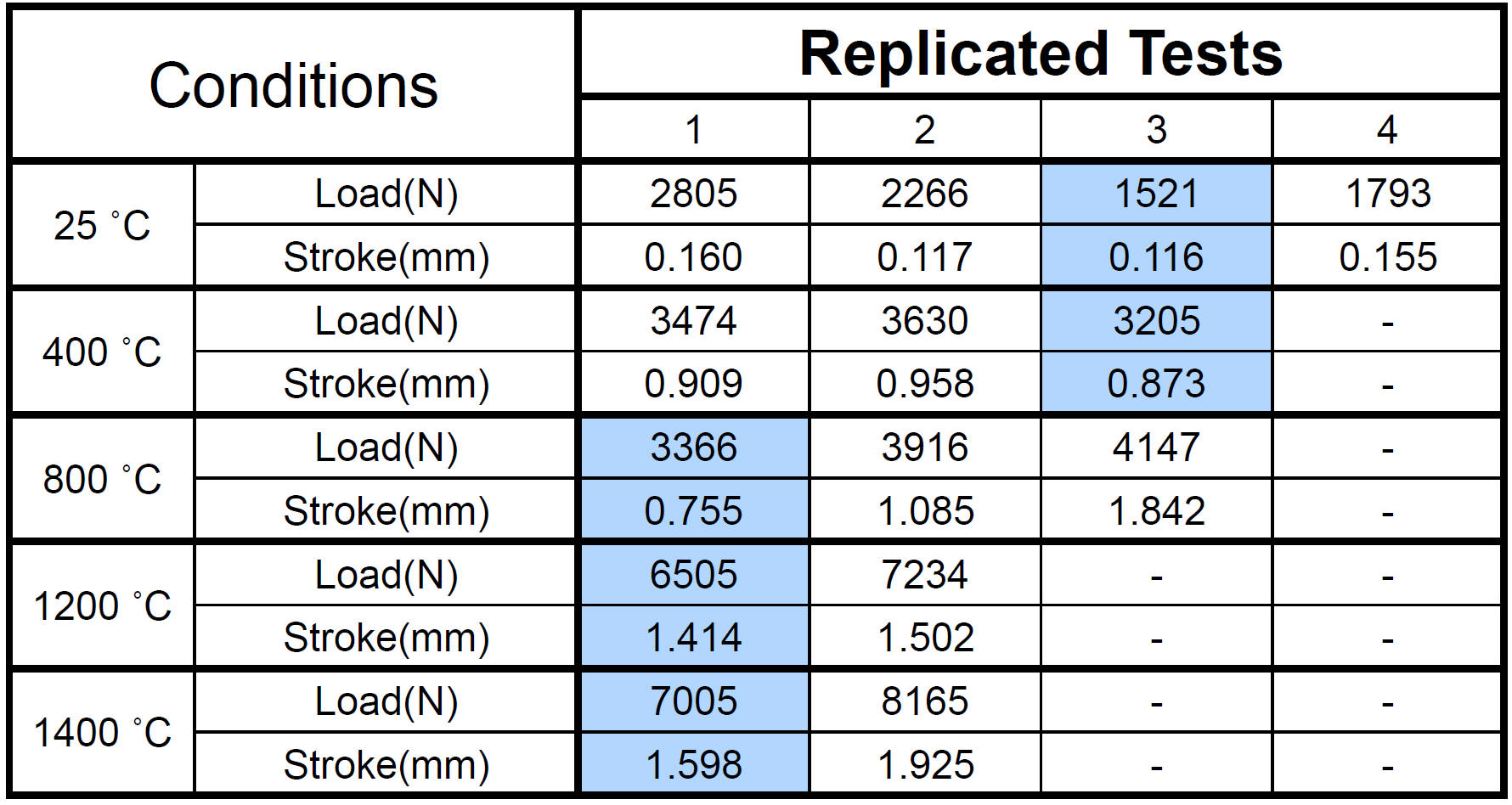
at Different Temperatures
The lowest final load at different temperature test is input to 2-D simulation
Load vs. Displacement Measurement/Prediction
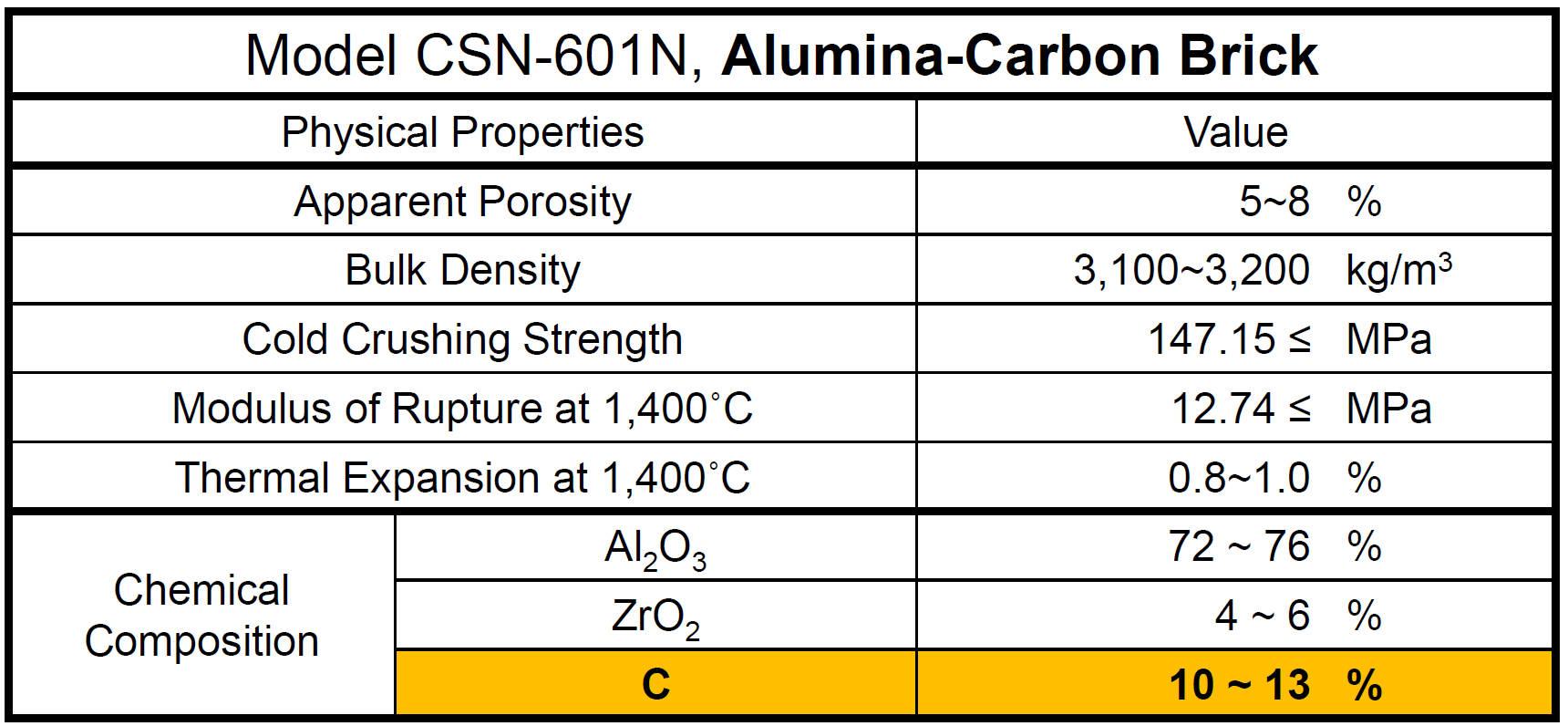
Physical Property of Ladle Plate
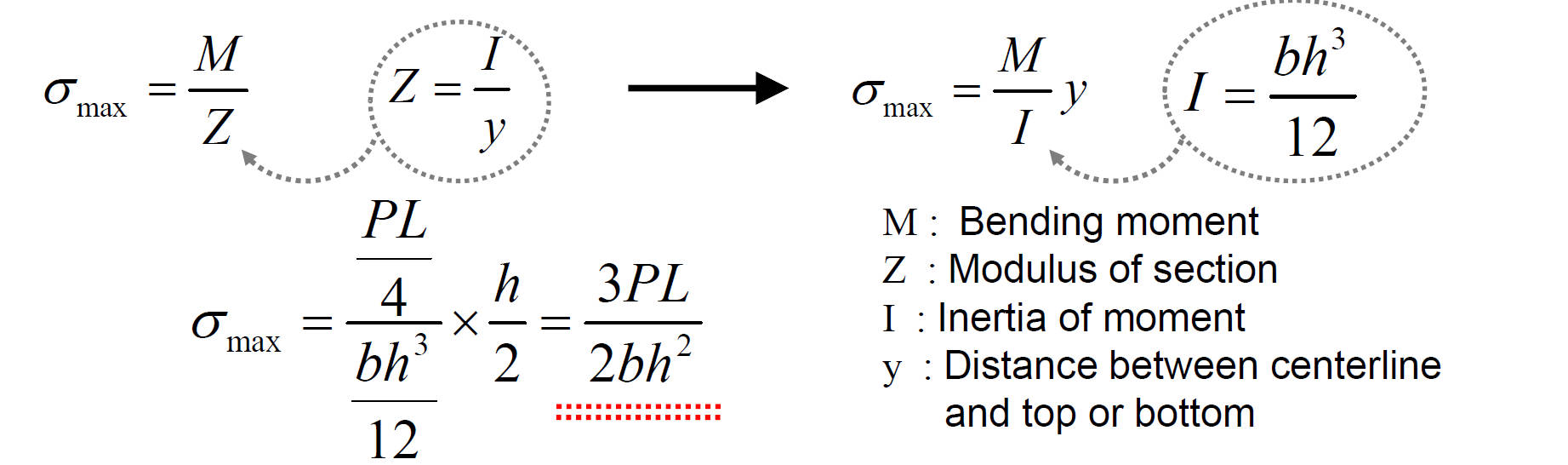
Analytical Solutions of 3-Point Bending Test
Elastic Modulus and Critical Tensile Strength Results
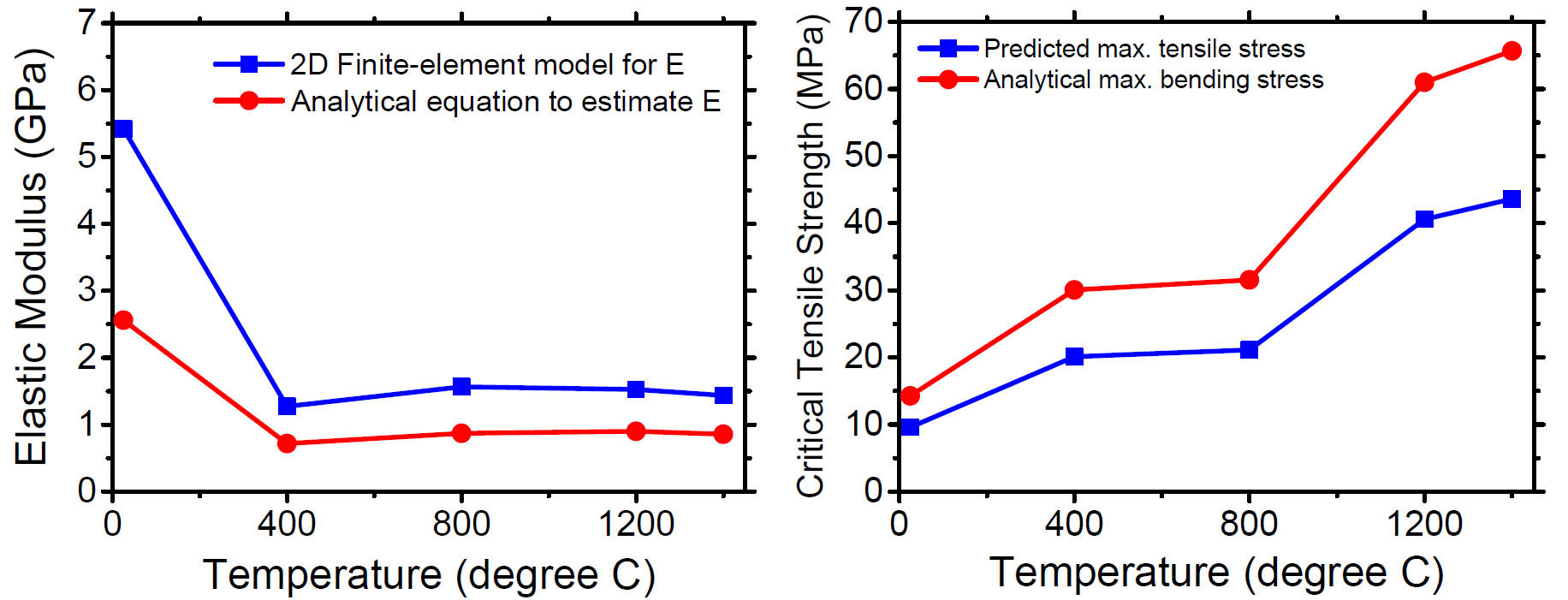
1.Apparent decrease in E with increasing temperature is likely due to creep during test (when temperature exceeds glass transition temperature of ceramic)
2.Predicted critical tensile strength is taken from FEM simulation at center-bottom of test piece (tension area)
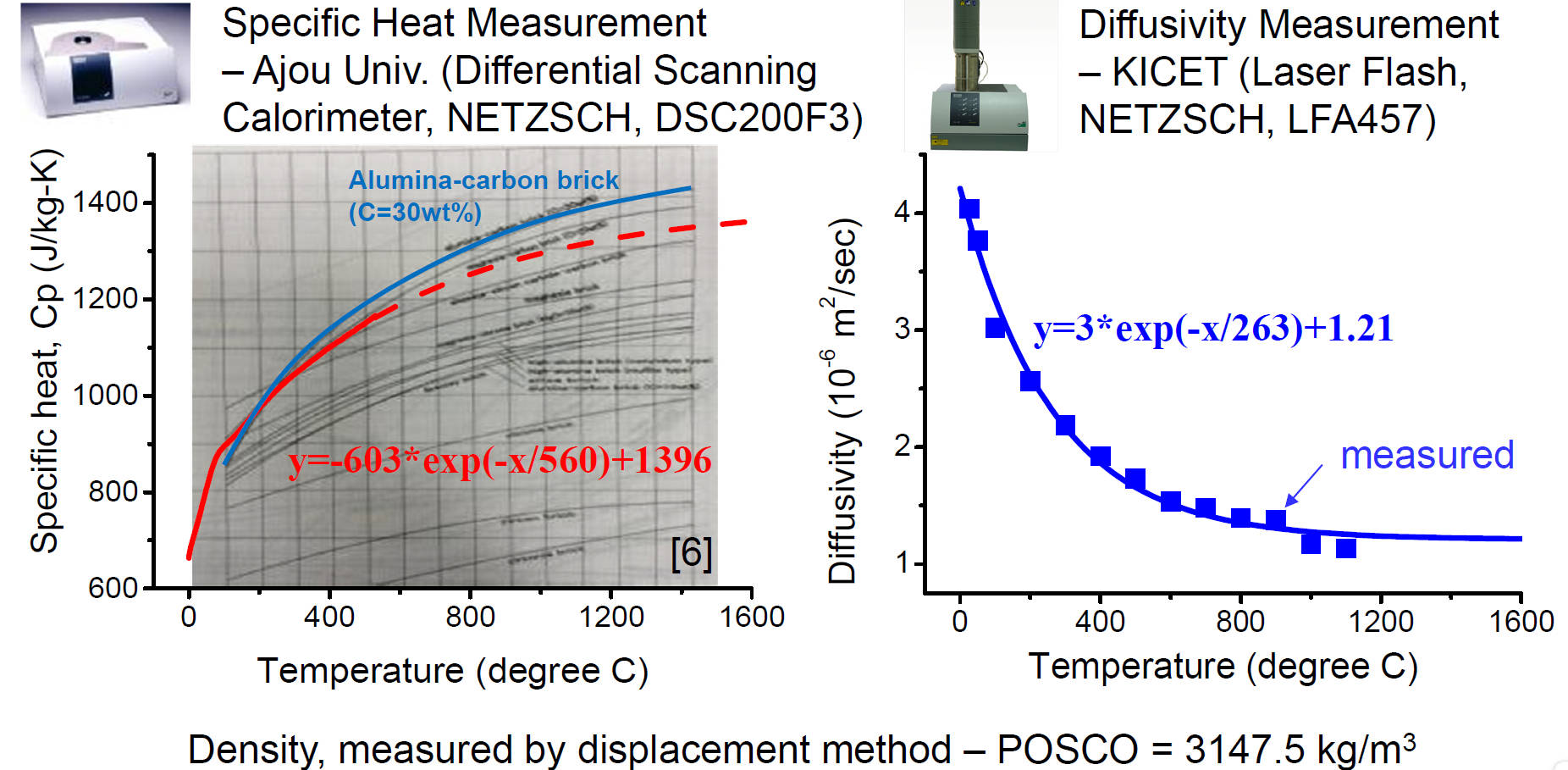
Thermal Property Measurements
Thermal Conductivity & Thermal Expansion Coefficient Evaluation
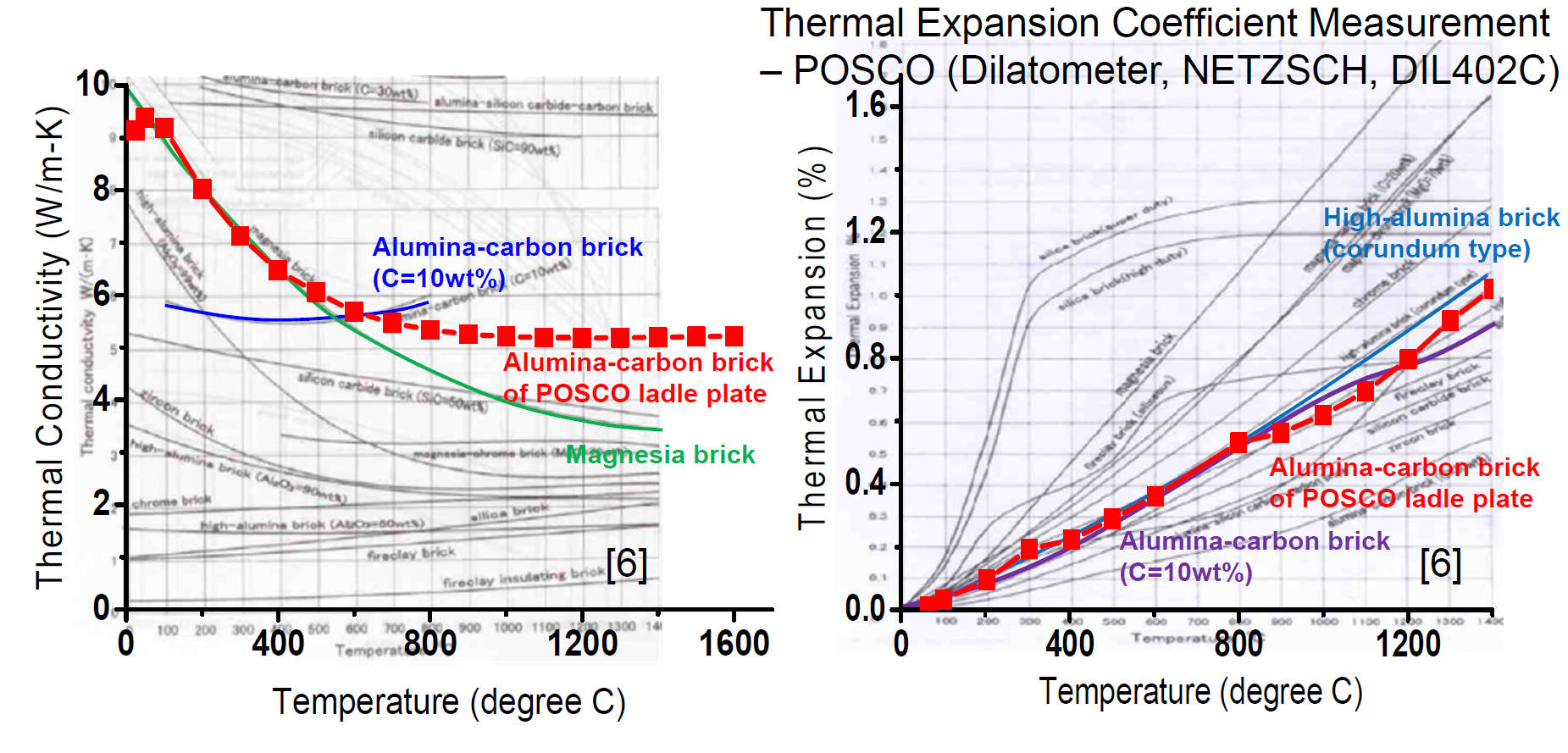
Measured thermal properties are well matched toreference data[6]
Ladle-Nozzle Sliding-Gate Components& Cassette Pressure Calculation
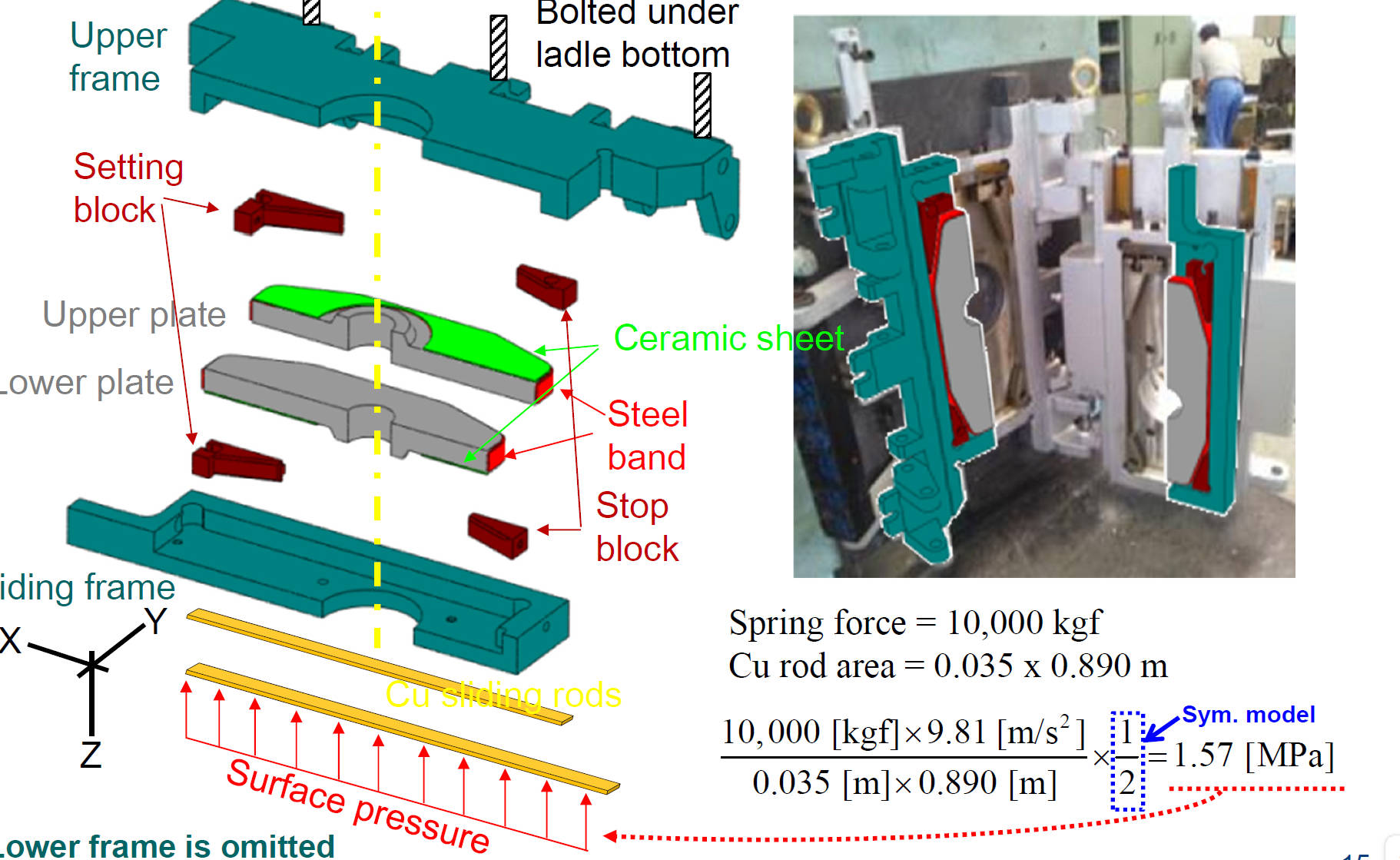
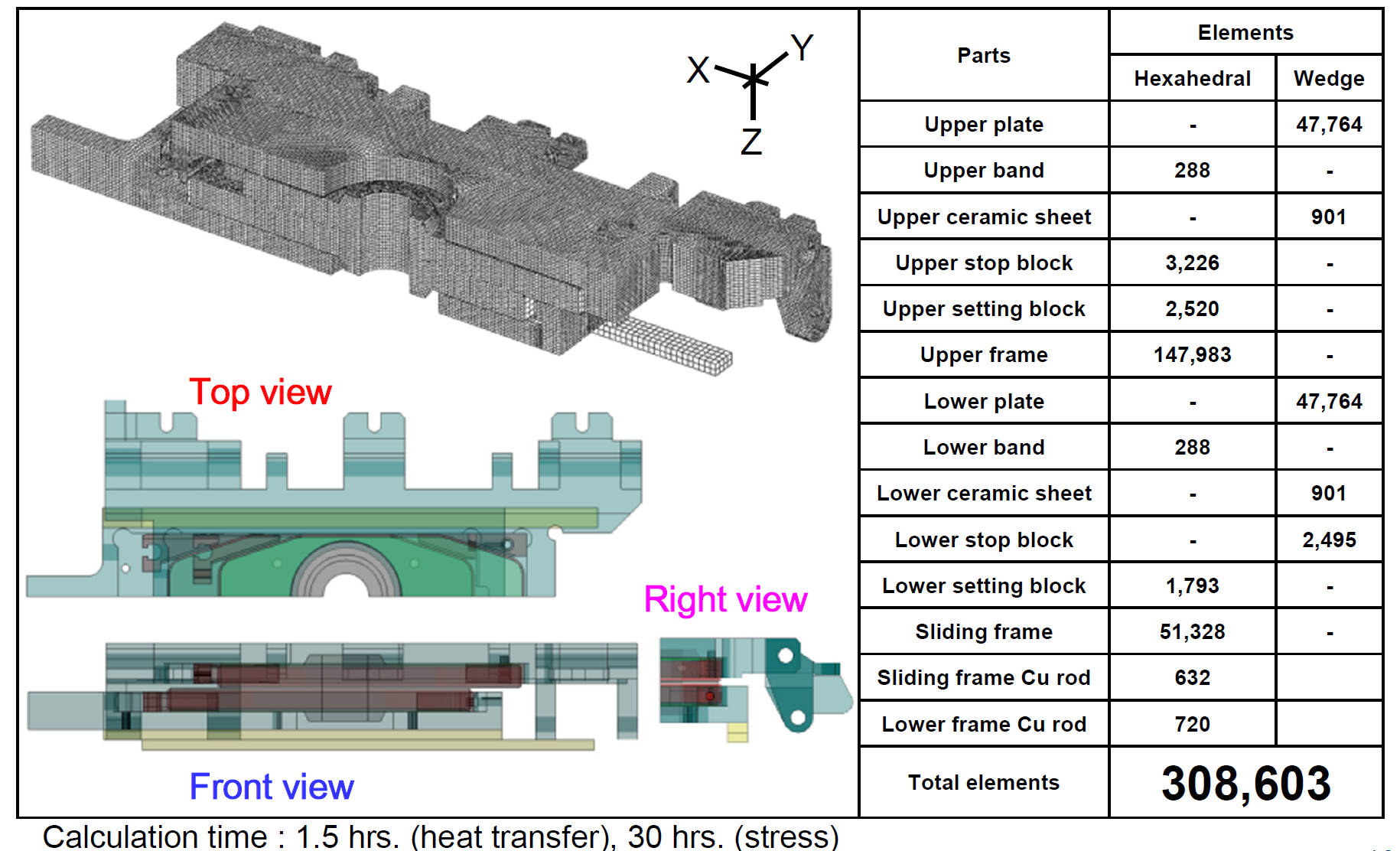
Ladle-Nozzle Sliding-Gate Domain / Finite Element Mesh
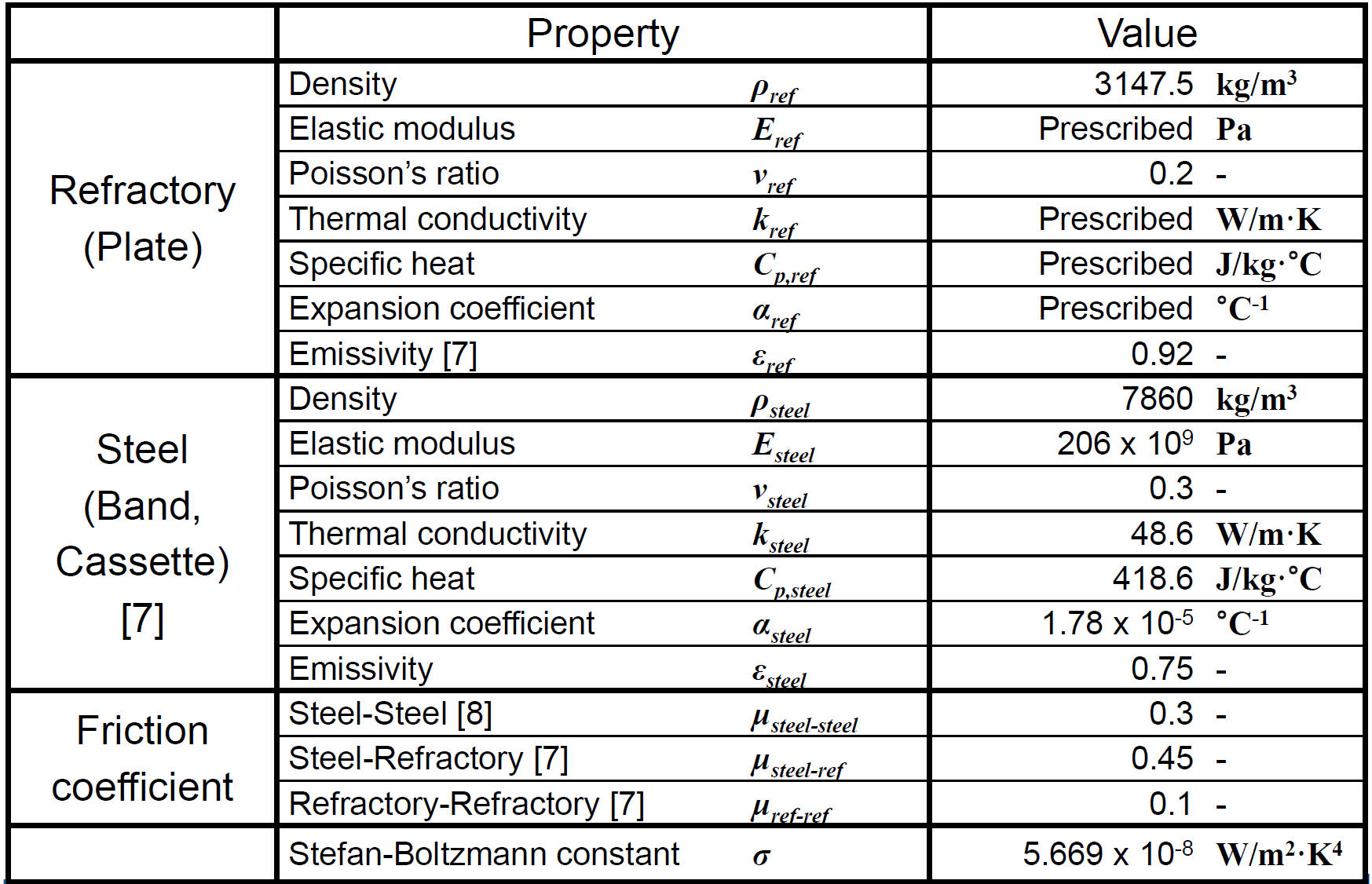
Properties for Ladle-Nozzle Sliding-Gate Model
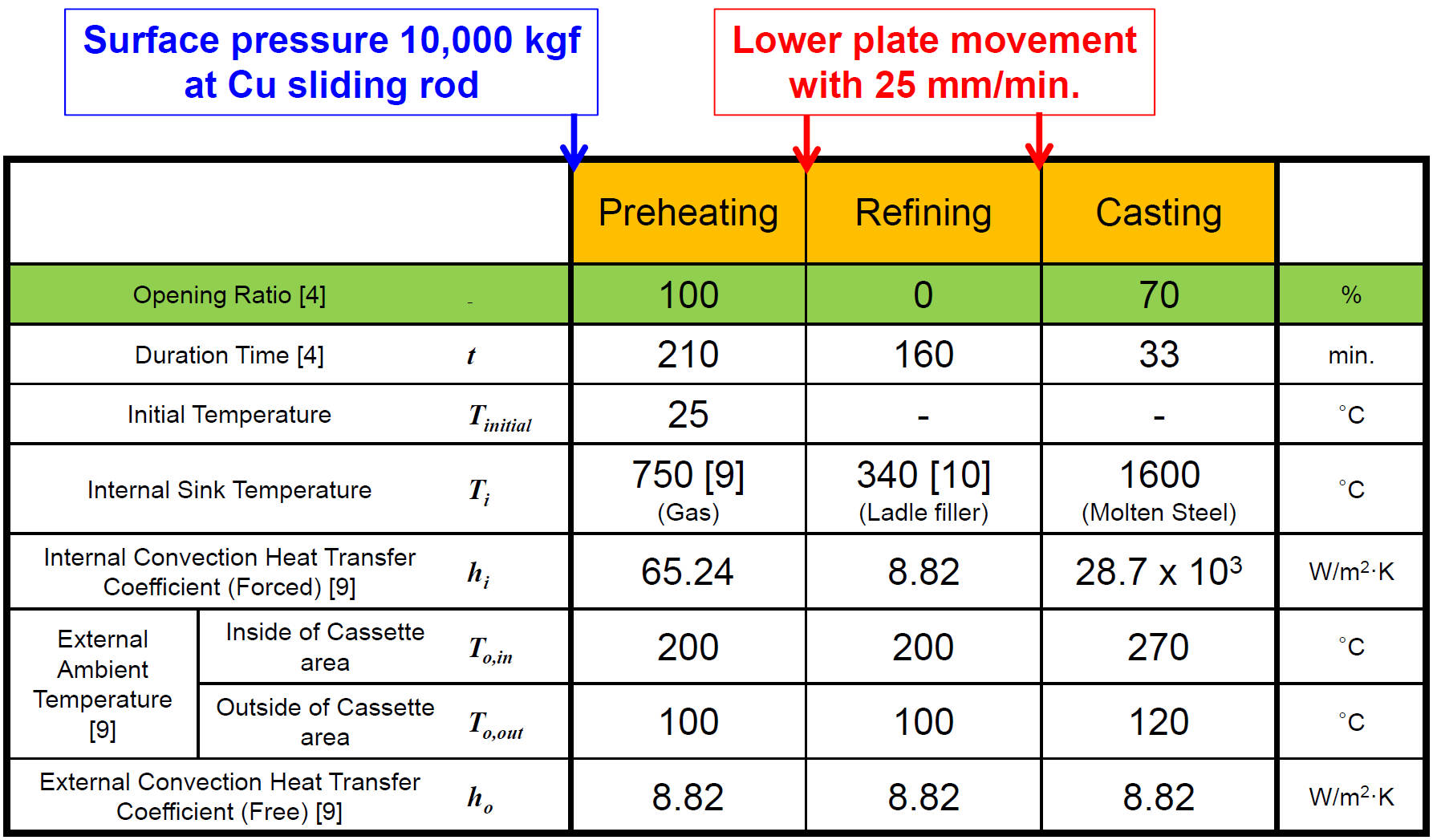
Variables and Boundary Conditions for Ladle Sliding-Gate Model
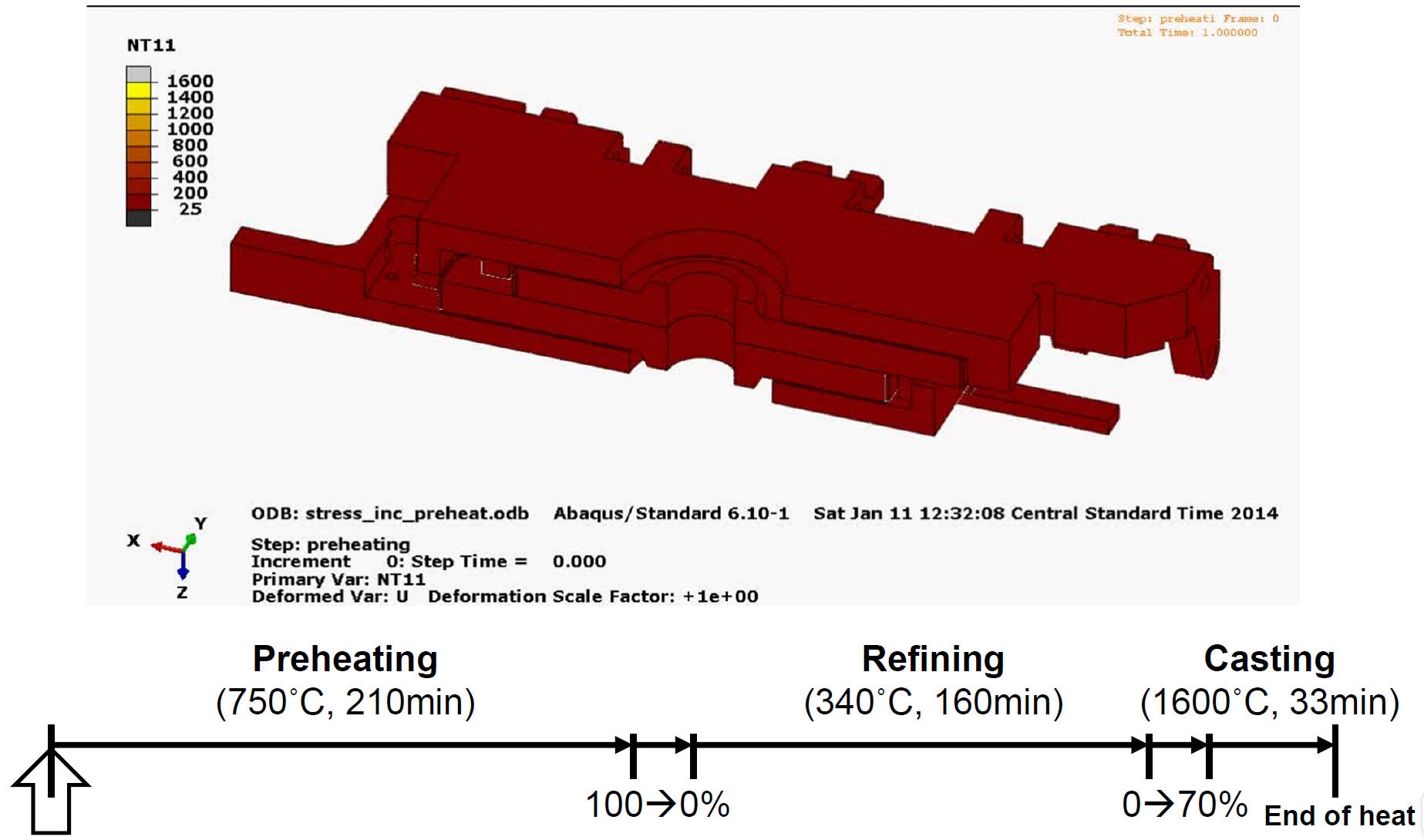
Thermal Behavior (Movie)
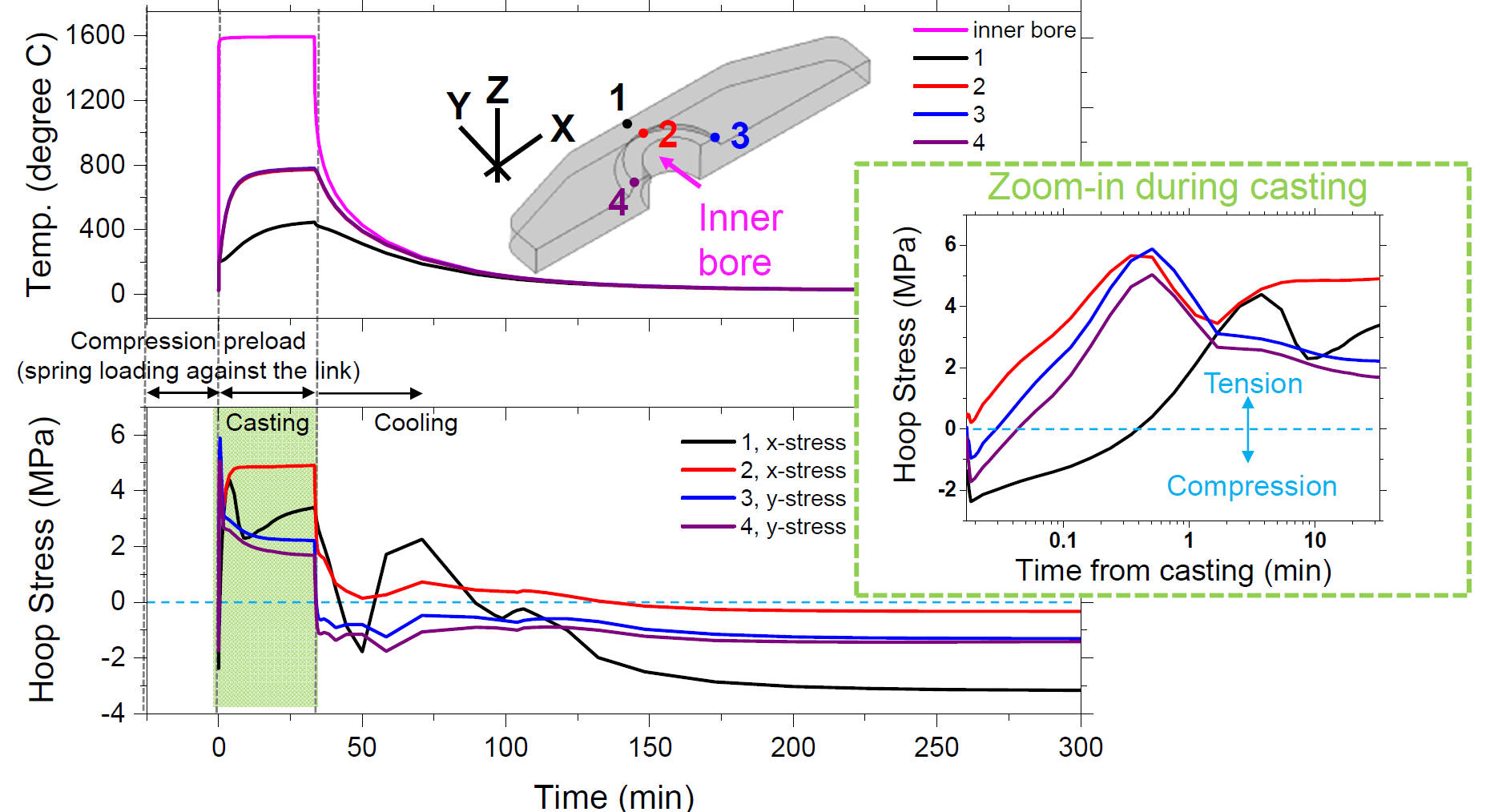
Temperature & Hoop Stress Histories at Locations where Cracks are Observed
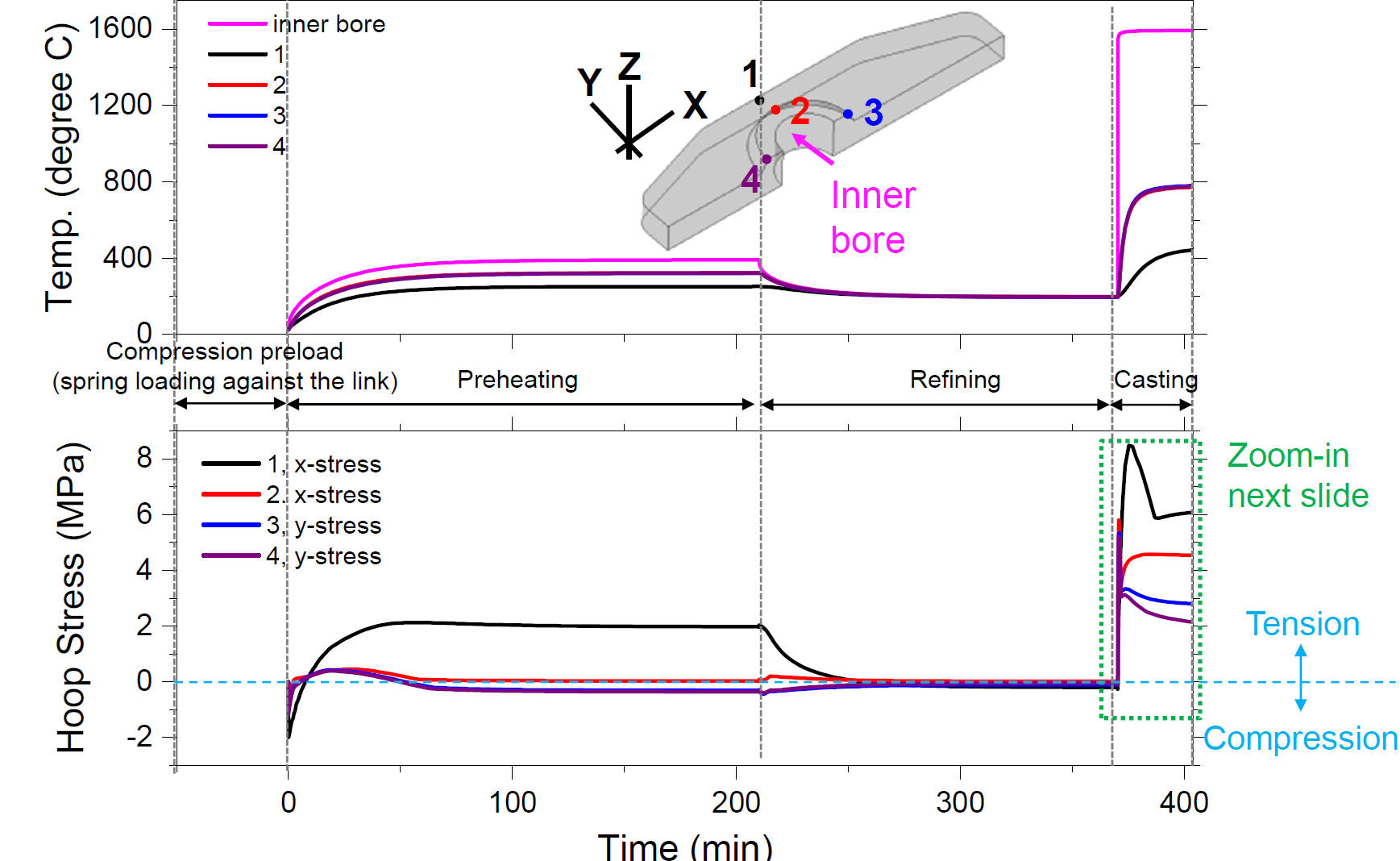
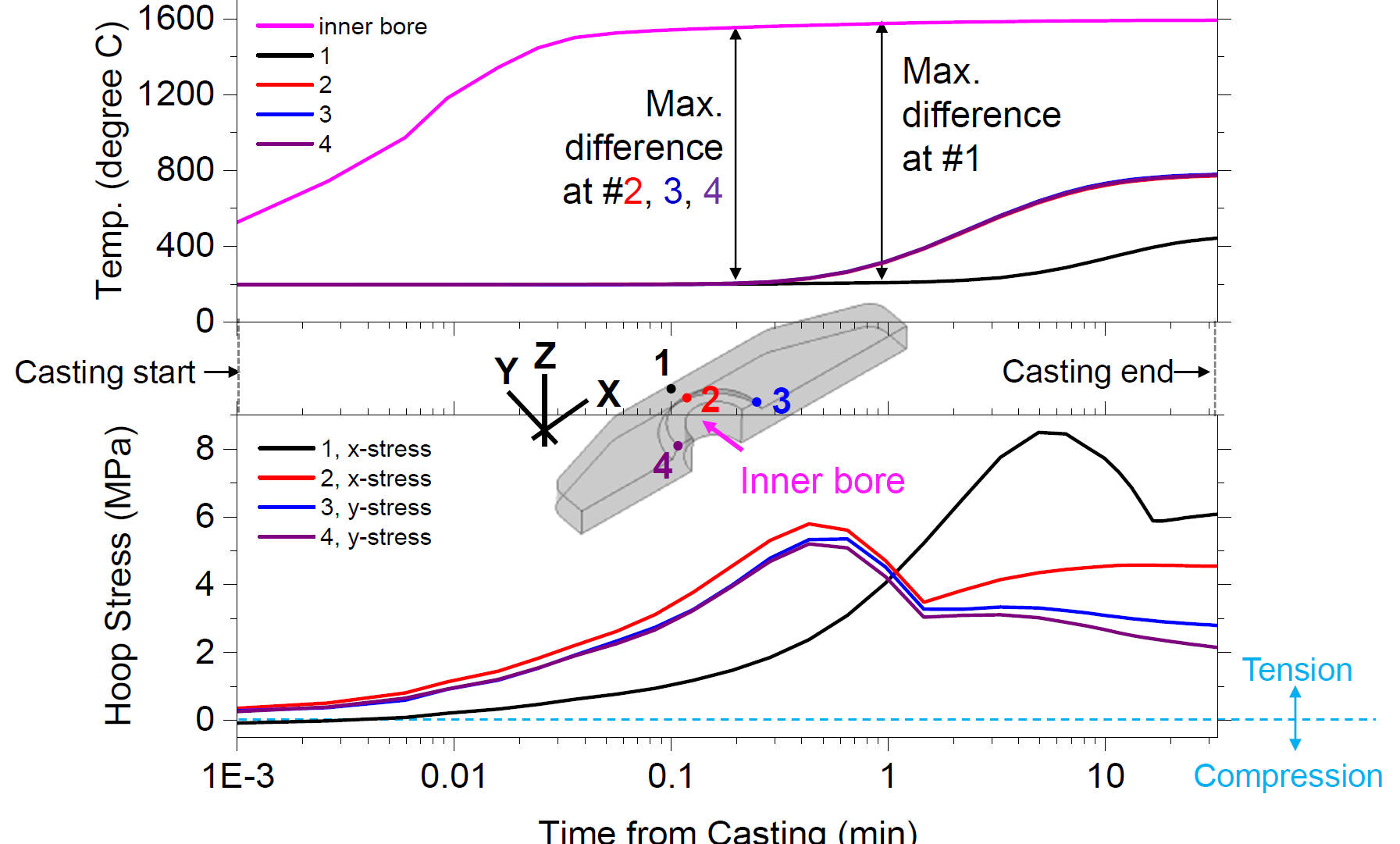
Temperature & Hoop Stress Histories during Casting (Log Scale on x-axis)
Common Through-thickness Crack Formation Mechanism
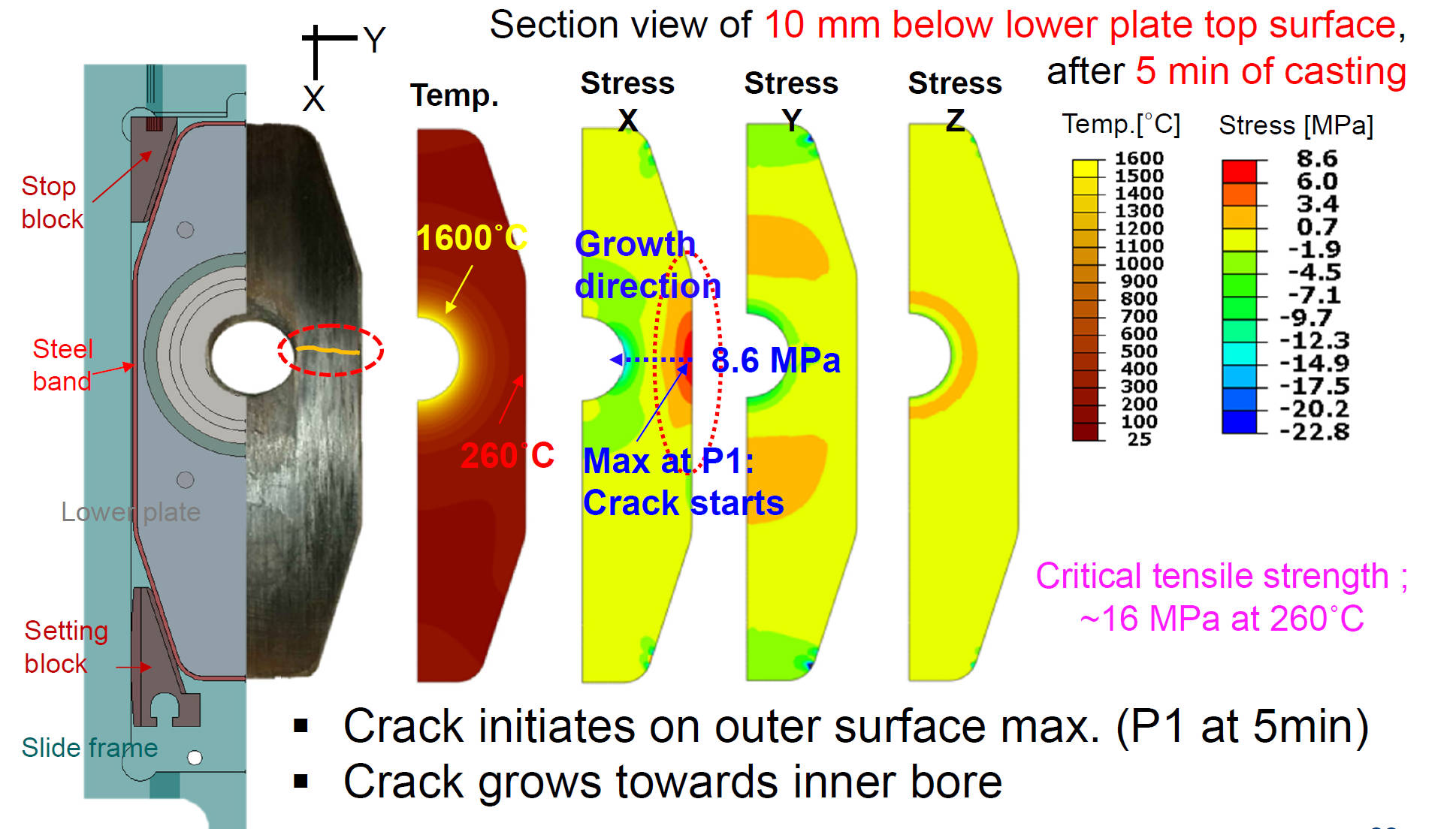
- Crack initiates on outer surface max. (P1 at 5min)
- Crack grows towards inner bore
Rare Radial Crack Formation Mechanism
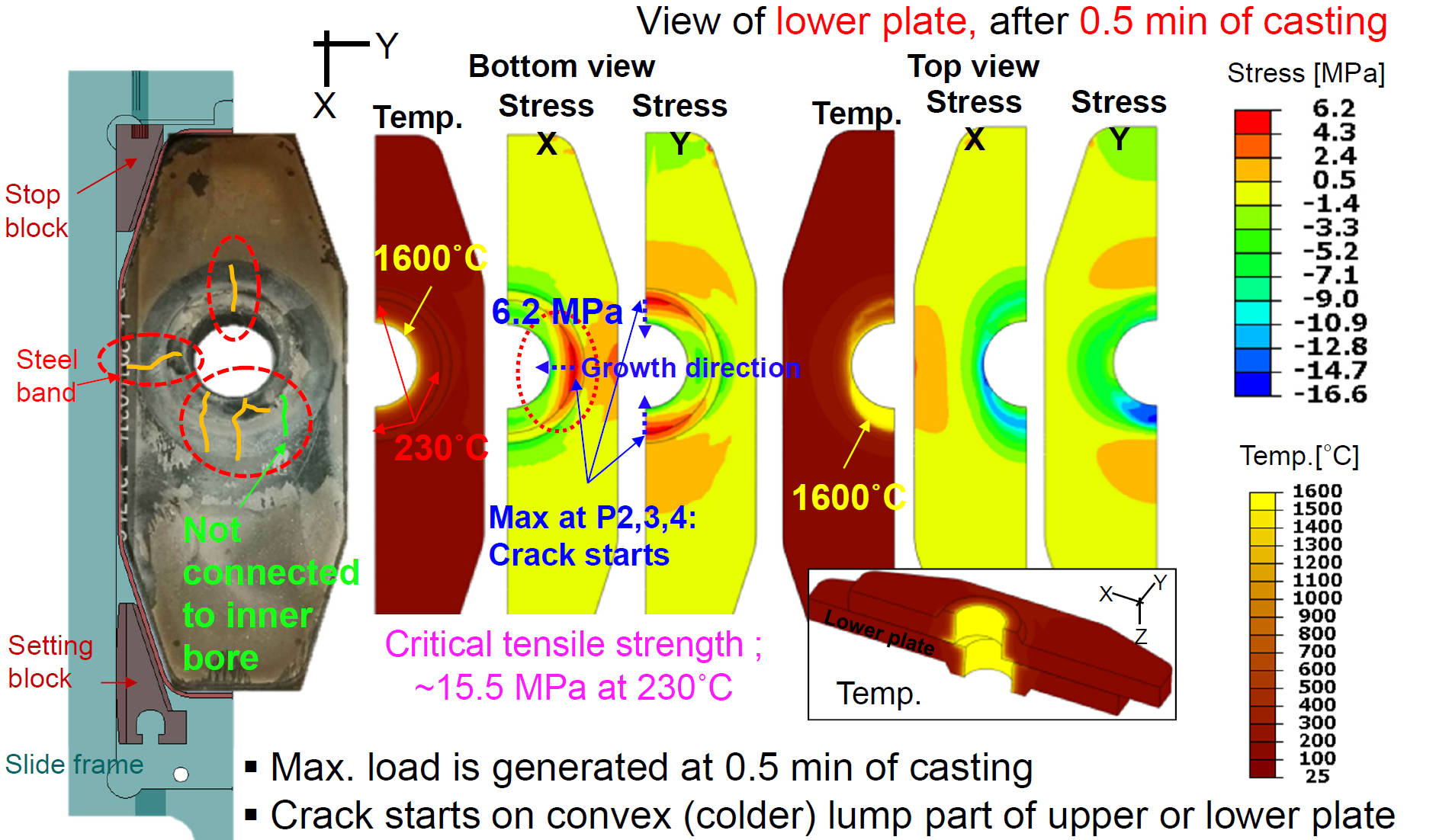
Mechanism
- load is generated at 0.5 min of casting
- Crack starts on convex (colder) lump part of upper or lower plate
Mechanical Loading Effects
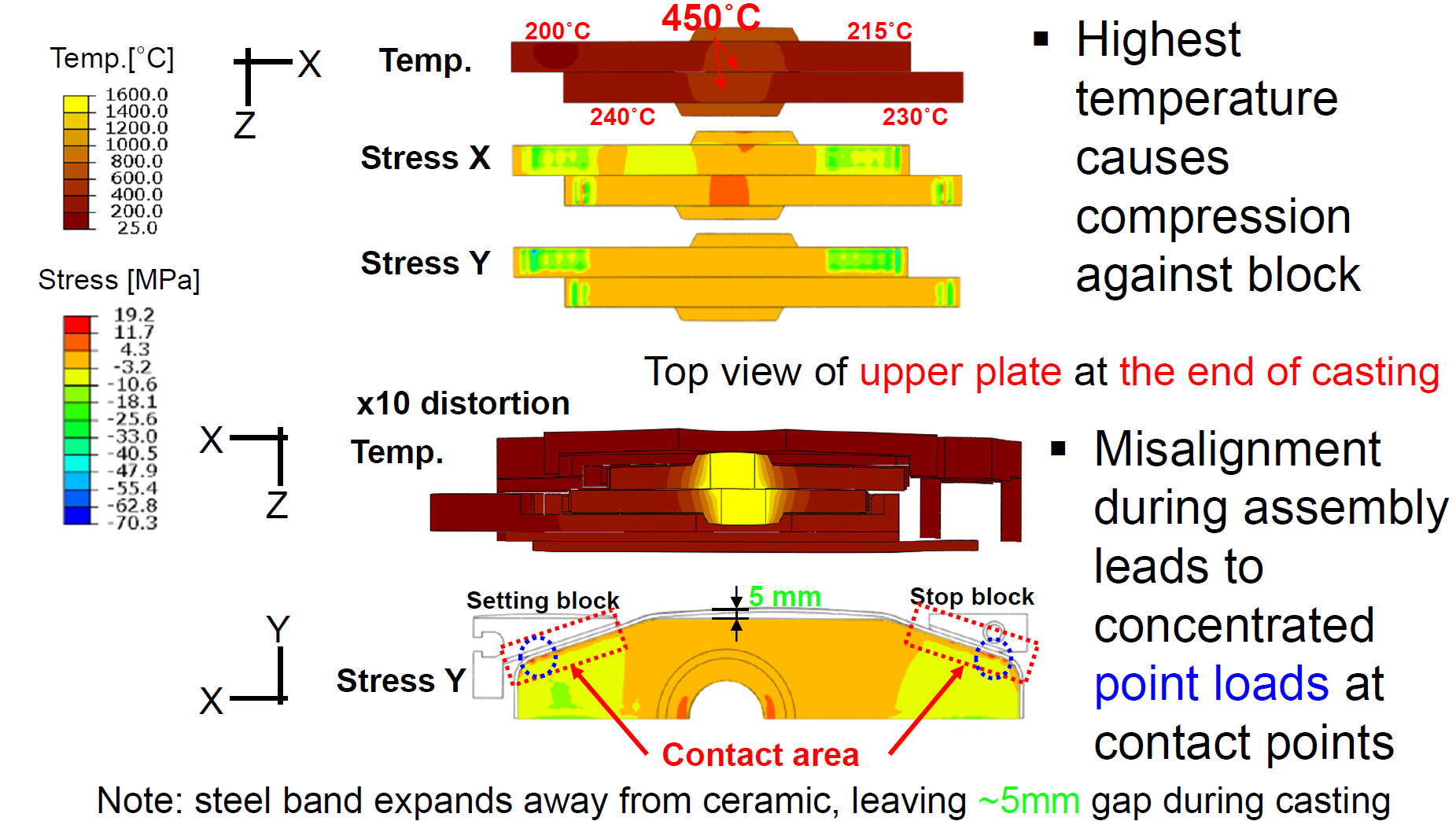
Temp. and stress distribution in plates at the end of castin
Casting Result without Preheating(Worst Case)
Direct casting and cooling is simulated without preheating for worst case
Thermal/Mechanical Distortion Affected by Cassette Pressure
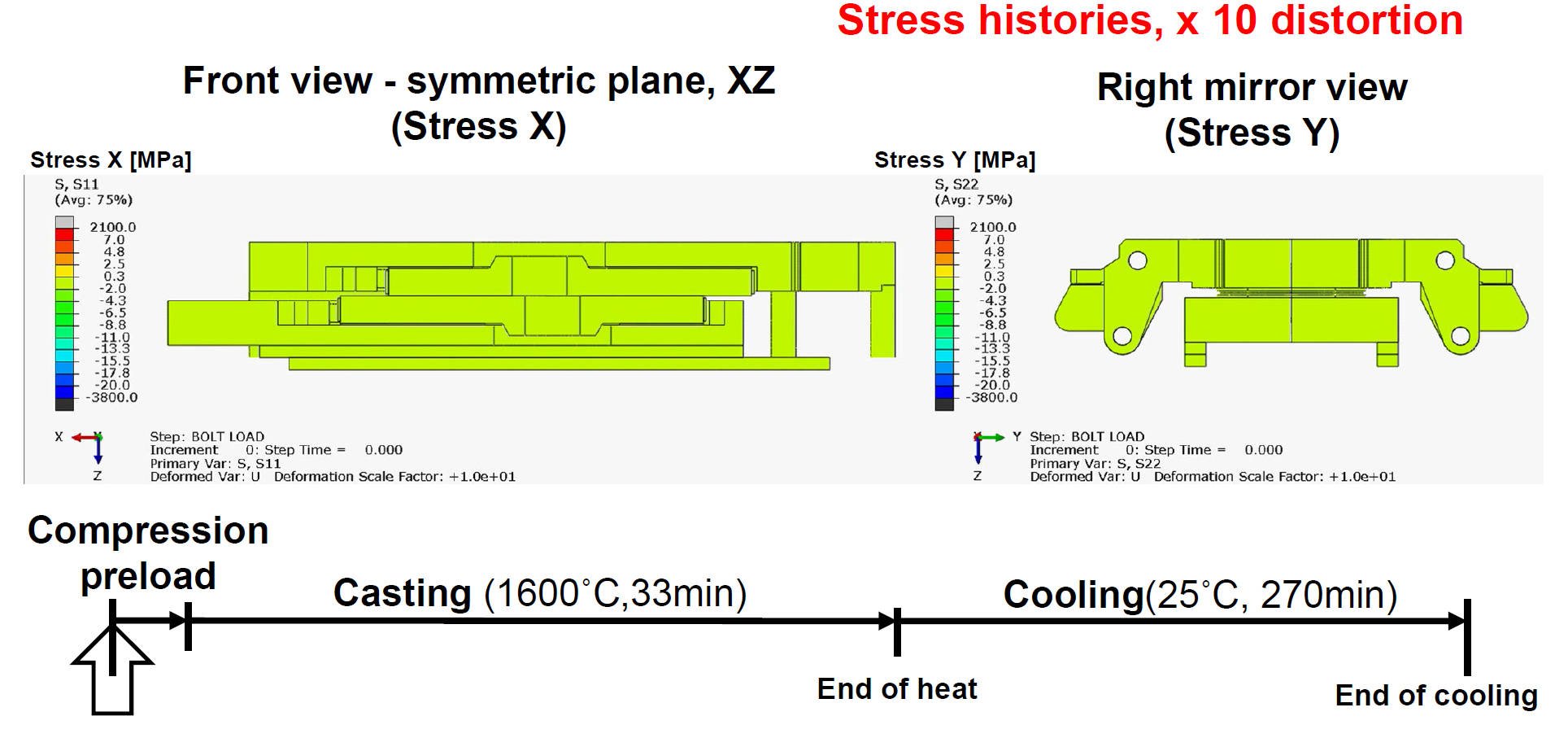
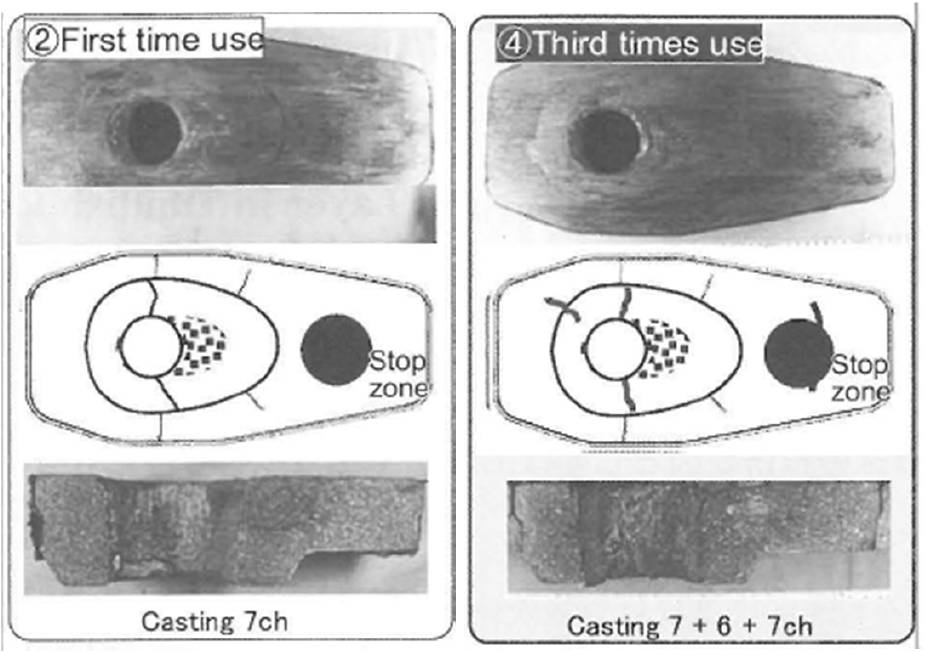
Cassette is plastically deformed after several times using for casting
according to plant engineer – Deformation shape effects of plate in the
plant will be discussed in future work
Future Works
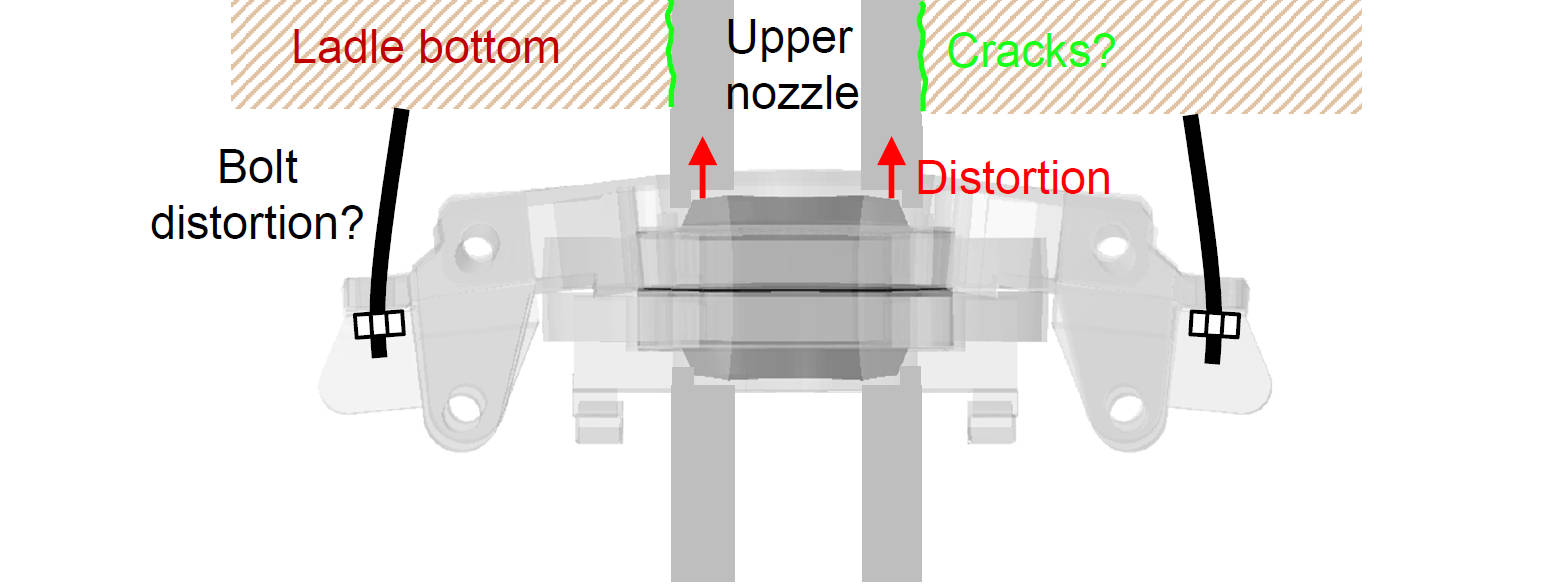
- Plastic deformation of used cassette in the plant is needed to investigate Thermal and mechanical distortion of ladle-nozzle system pushes against upper nozzle, creating forces between upper nozzle and ladle bottom refractory.
- Creep effect in ceramic materials is important for cracking
Reusable Ladle-Nozzle Sliding-Gate Domain/ Finite Element Mesh
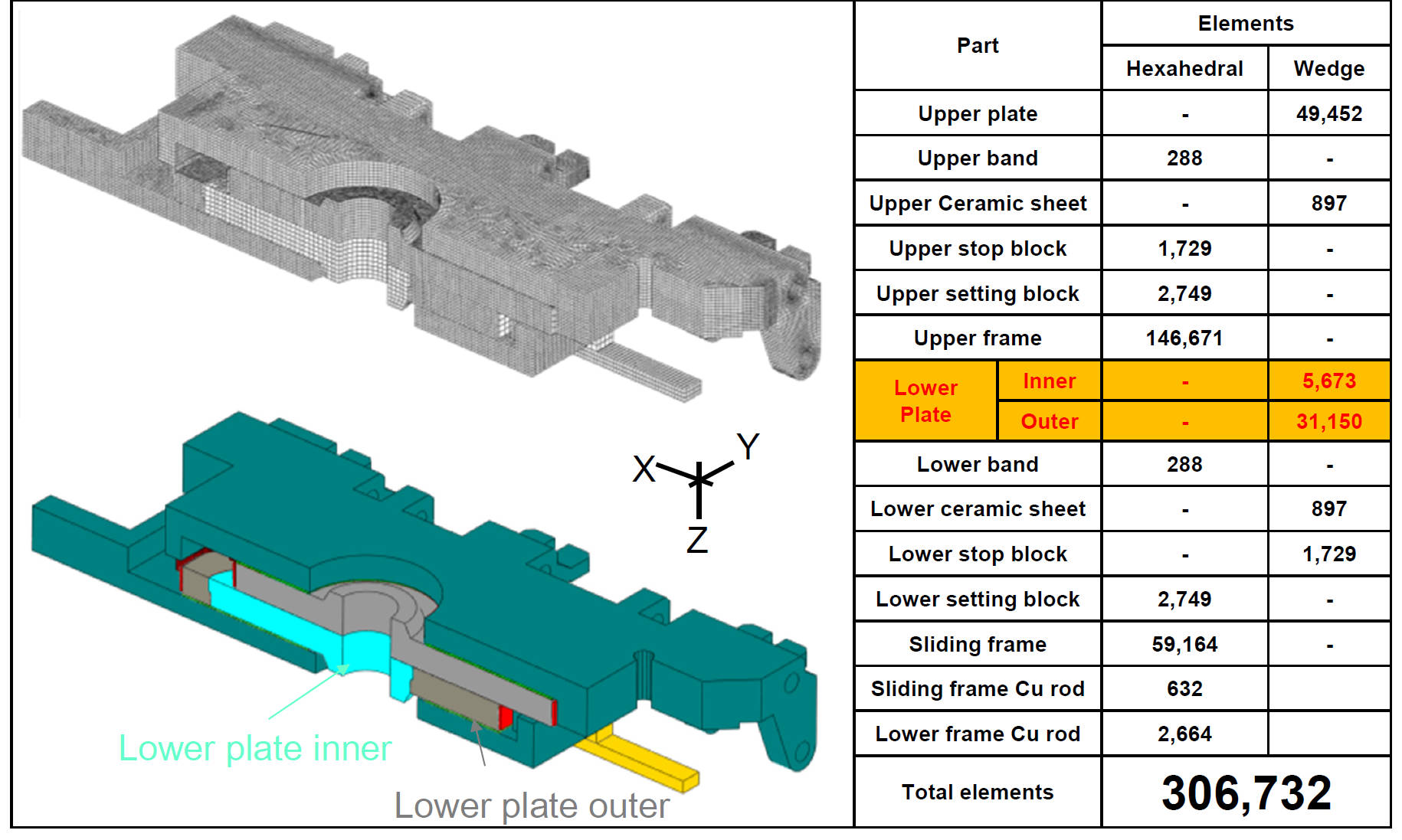
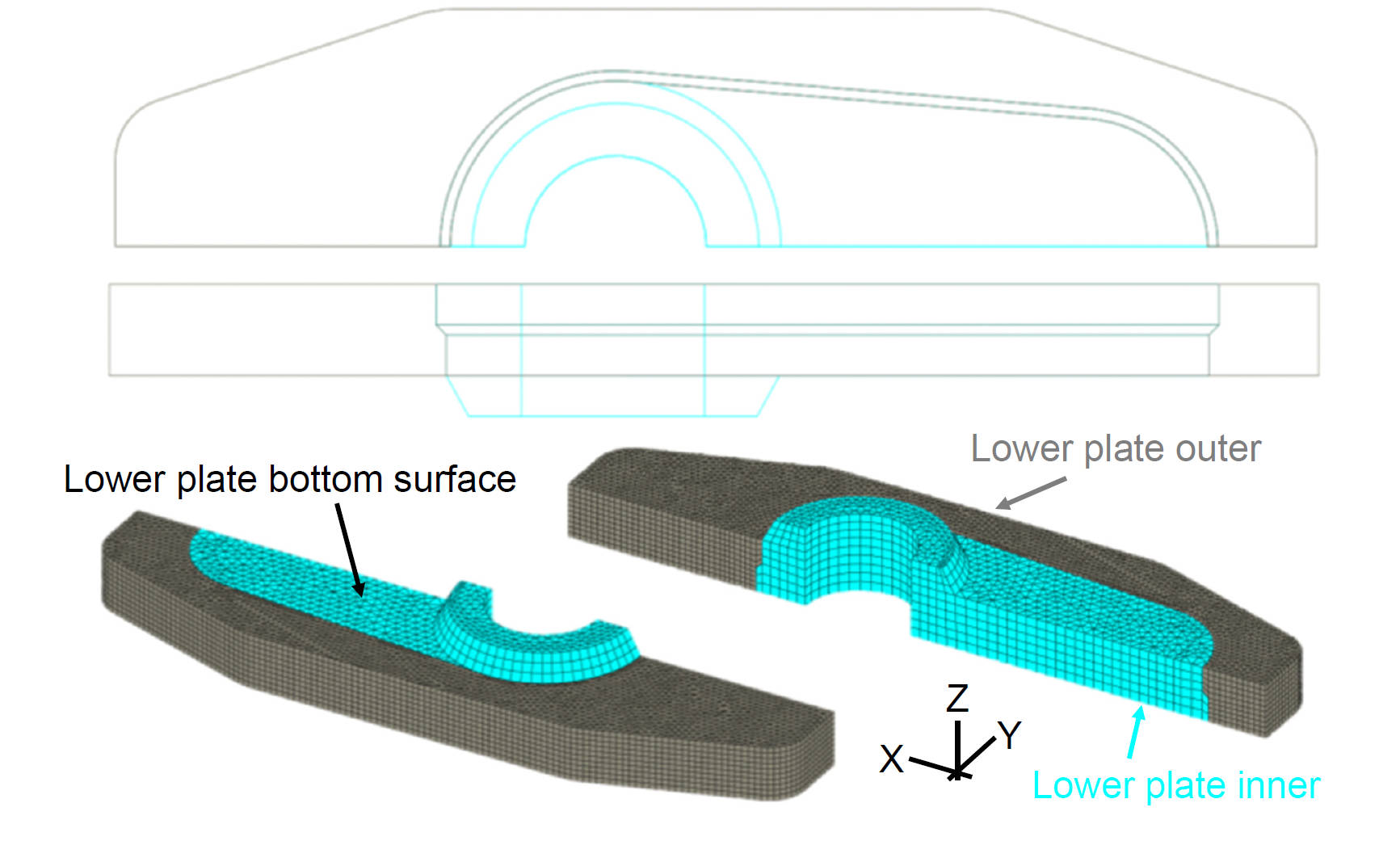
Reusable Lower Plate Domain / Finite Element Mesh
Hoop Stress Results Comparison(Conventional / Reusable)
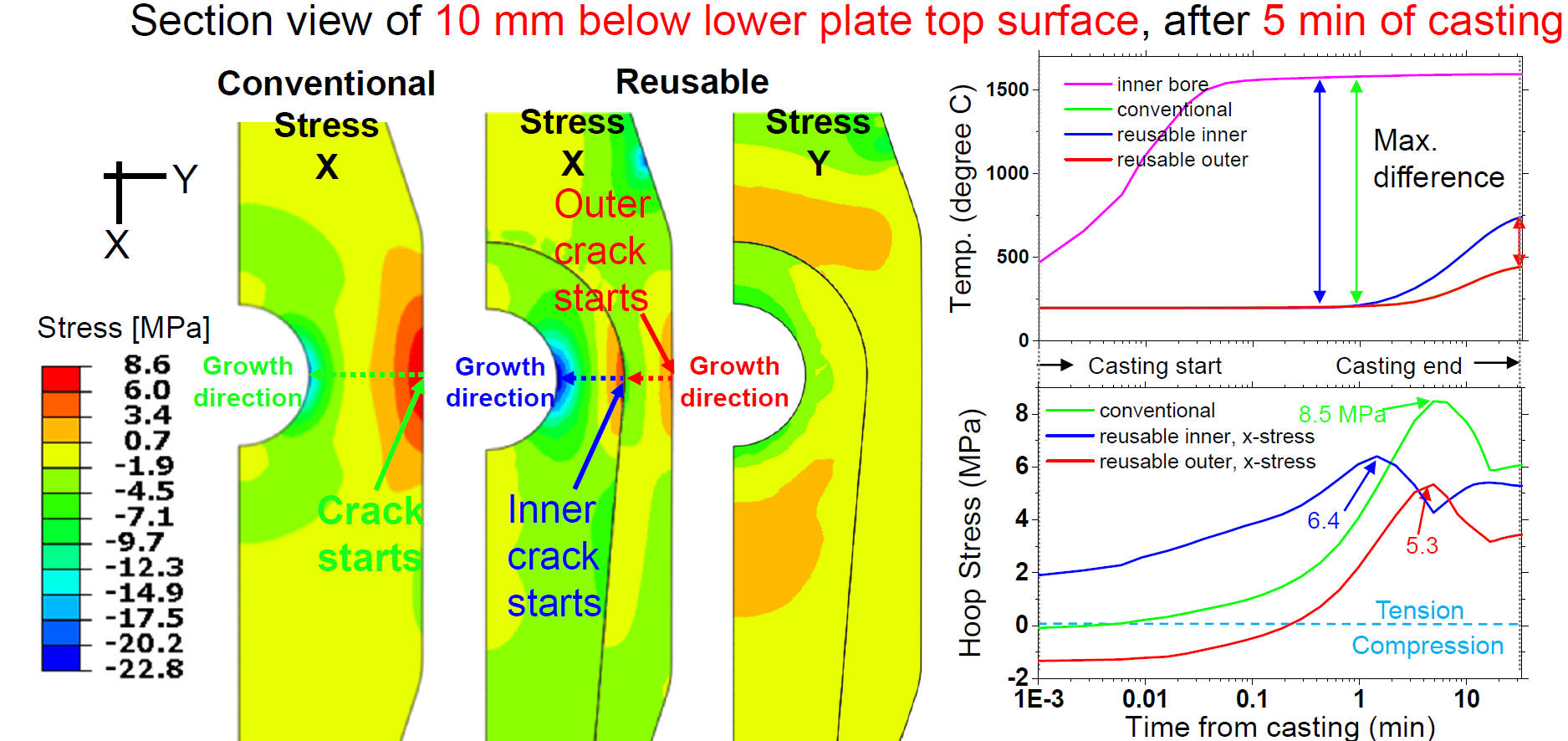
- Larger temperature difference between inside and outside
surfaces generates larger tensile stress
- Tensile stress can be reduced by using outer “reusable” plate
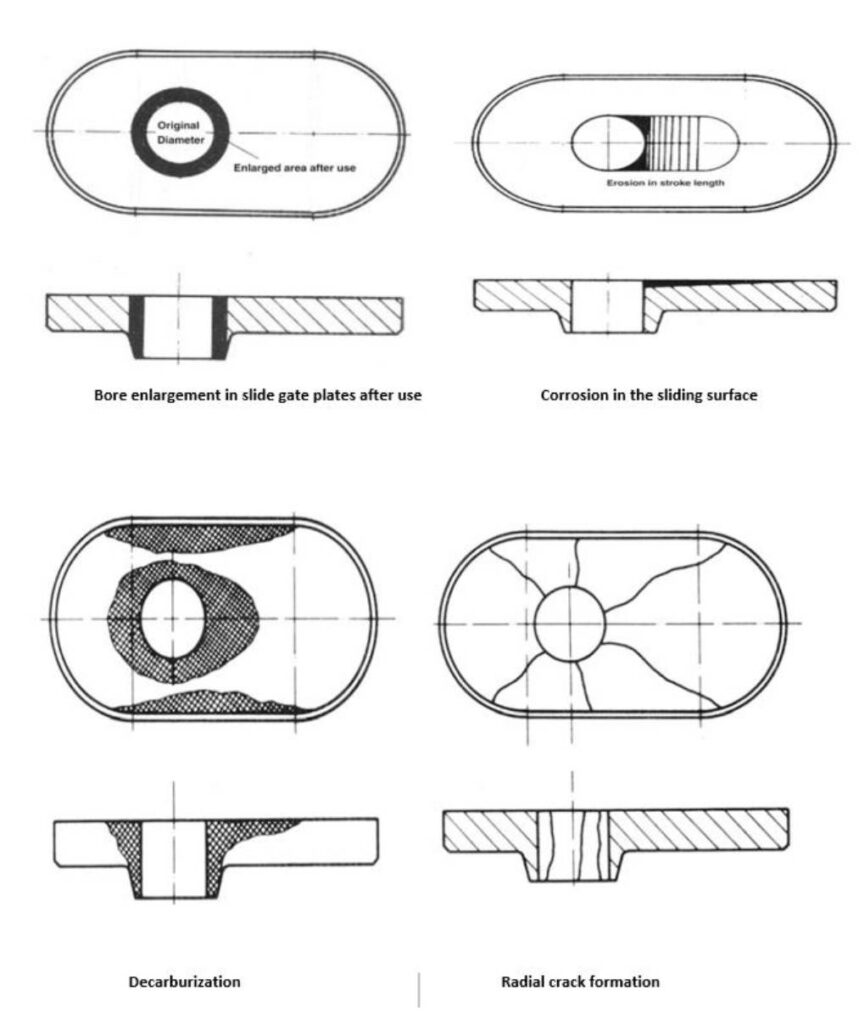
Reusable Lower Plate Outer Crack Formation Mechanism
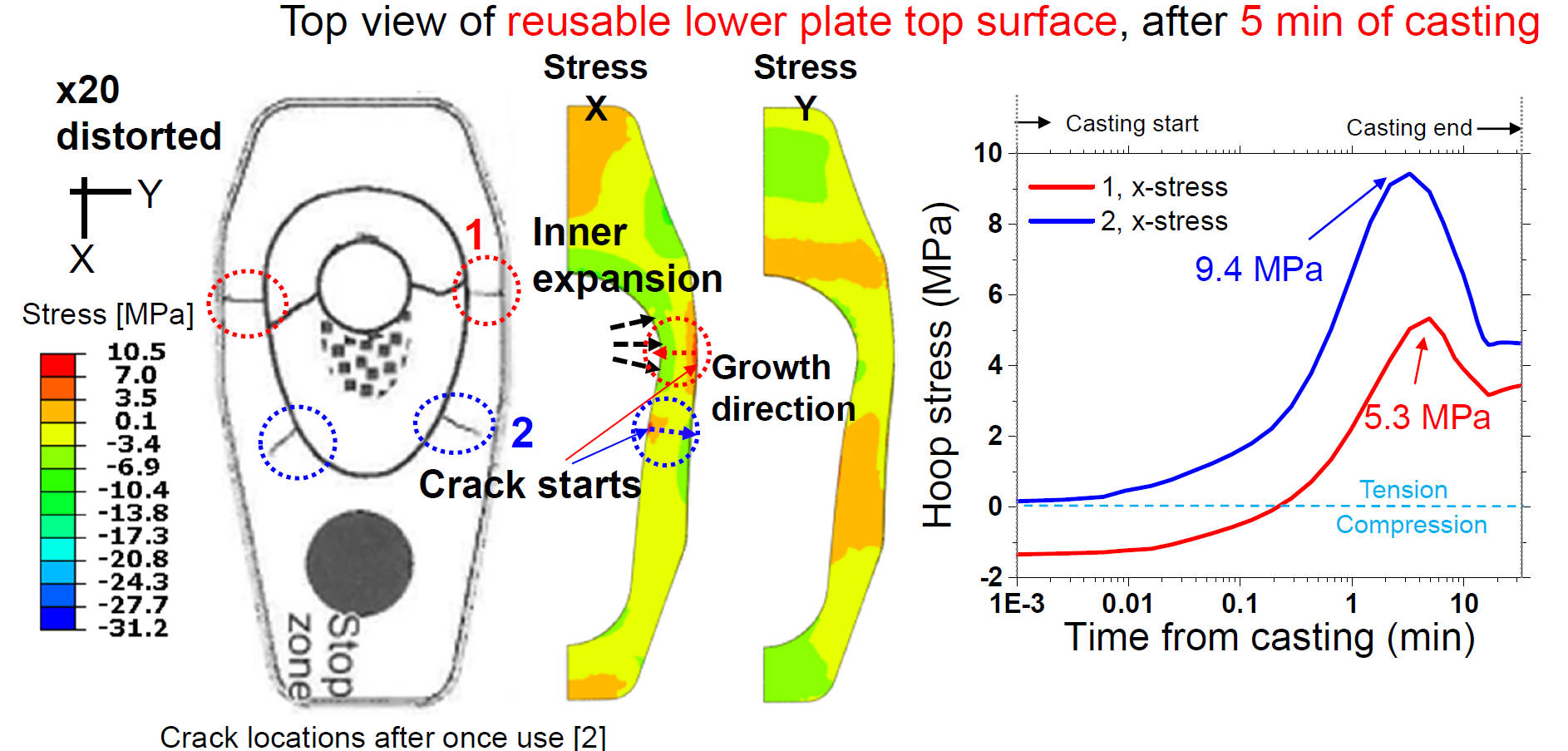
Crack Formation Mechanism
- Crack locations are well matched to used plate
- In addition to same common crack mechanism: Expansion of inner plate causes tension in reusable outer plate
Conclusions
- Replicated 3-point bending tests measured refractory strengths at different temps.
- Thermal expansion of hot inside of plate causes exterior tensile hoop stress and crack growth towards interior: leading to both common through thickness cracks (starting at cold outside of plate) and rare radial cracks (starting at cold outside of lump).
- No cracks are predicted so quantitative models and fracture criteria need more work.
- Reusable plate are predicted to reduce tensile hoop stress, but through-thickness crack formation may be unavoidable.
- Two different crack mechanisms can form through thickness cracks in reusable outer plate middle.