Introduction
In continuous casting operations, the ladle shroud gasket is a small but critical component that ensures a safe and sealed connection between the ladle and the ladle shroud. While the ladle shroud itself controls the molten steel flow from ladle to tundish, the gasket provides the essential sealing and thermal protection that make smooth and oxidation-free casting possible.
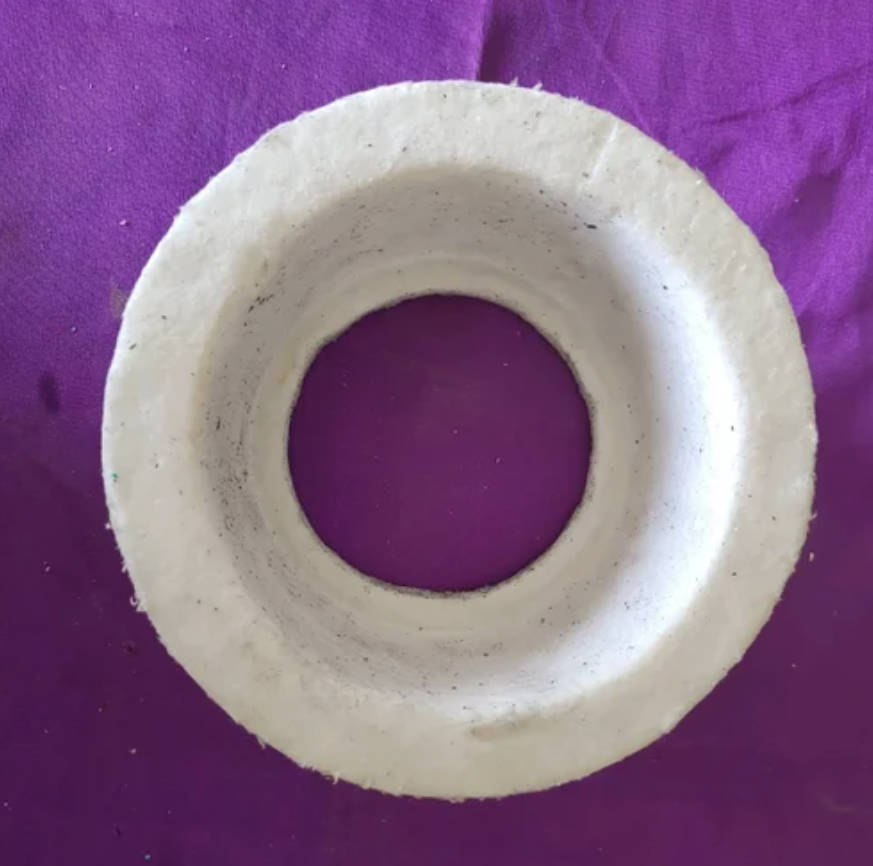

This article introduces the material, function, shapes, installation method, and production process of ladle shroud gaskets, helping operators and engineers better understand their role in modern steelmaking.
1. What Is the Material of Ladle Shroud Gasket?
The ladle shroud gasket is made from high-temperature-resistant, compressible, and non-stick refractory materials that can maintain strength and flexibility even under extreme heat. The choice of material depends on the temperature, ladle design, and sealing method.
Common Materials Used:
- Ceramic Fiber Paper or Board
Ceramic fiber gaskets are the most common choice. They provide excellent thermal insulation and can withstand temperatures from 1260°C to 1430°C. The material is flexible, easy to cut, and ensures tight sealing between the ladle and shroud. - Graphite Composite Gasket
Graphite gaskets are ideal for high-pressure or high-temperature casting environments. They have strong compressive strength, oxidation resistance, and chemical stability, making them suitable for long casting sequences. - Non-Asbestos Fiber Gasket
To replace traditional asbestos materials, modern gaskets use non-asbestos composites reinforced with aramid or glass fibers. These materials are safe, environmentally friendly, and maintain good elasticity and heat resistance. - Microporous Insulation Sheet
Some gaskets use microporous insulation boards for higher heat resistance and energy efficiency. These materials help reduce heat transfer from the ladle to the shroud interface.
All these materials ensure that the ladle shroud gasket maintains its sealing ability under both mechanical stress and high temperature, protecting the ladle nozzle and shroud during continuous casting.
2. Function of Ladle Shroud Gasket
Although small, the ladle shroud gasket performs several critical functions in steelmaking operations:
- Sealing Protection
The gasket provides an airtight seal between the ladle’s bottom nozzle and the ladle shroud head. It prevents air aspiration into the molten steel stream, reducing oxidation and inclusion formation. - Thermal Insulation
It acts as a buffer against temperature differences between the hot ladle and the shroud, preventing thermal shock cracking at the connection area. - Mechanical Cushioning
During installation, the gasket absorbs vibrations and mechanical stresses, protecting the refractory contact surfaces from damage. - Leak Prevention
A properly installed gasket fills surface irregularities and prevents molten steel leakage from the ladle-shroud interface — an essential safety measure. - Easy Replacement
The gasket simplifies shroud mounting and removal, ensuring smooth and efficient operations between casting heats.
Overall, the ladle shroud gasket is essential for maintaining safe, clean, and efficient continuous casting.
3. Shapes of Ladle Shroud Gaskets
Different ladle shroud types require different gasket designs. The shape of the ladle shroud gasket is customized according to the shroud’s upper head structure and the ladle nozzle system.
Common Shapes Include:
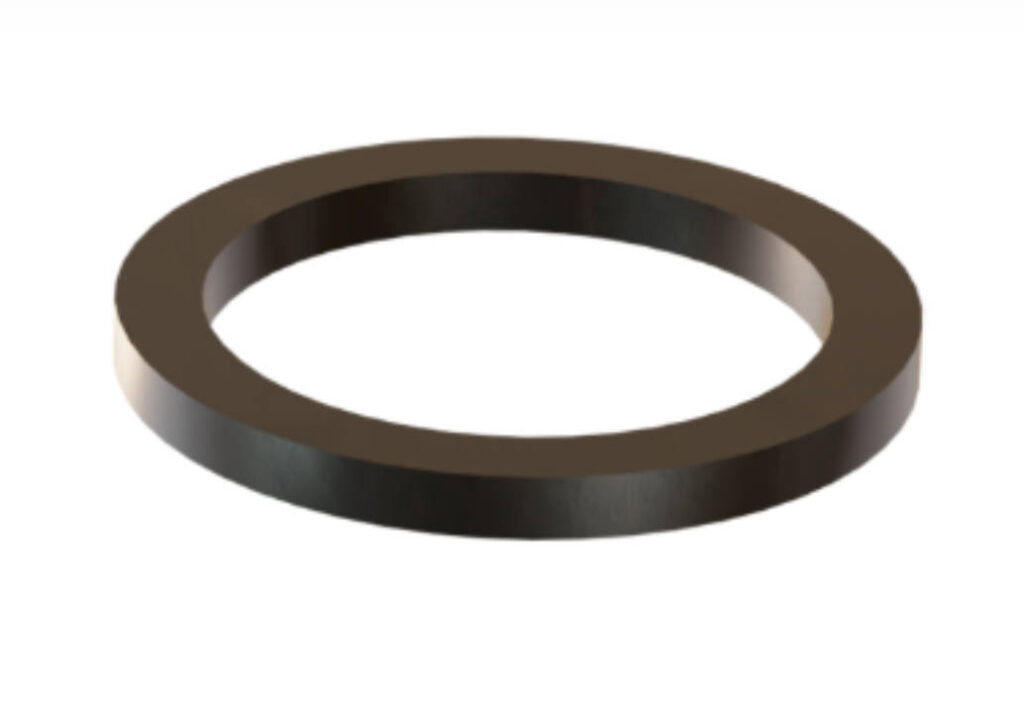
- Flat Ring Gasket
The most widely used design — a simple round gasket with an inner and outer diameter matching the shroud and ladle seat. It offers uniform compression and easy installation. - Stepped Ring Gasket
Designed with a step or groove to match irregular or layered joint surfaces, ensuring tighter sealing. - Conical Gasket
Used when the ladle shroud has a tapered head. The gasket is cut at an angle to ensure full surface contact and airtight sealing. - Segmented or Split Gasket
When quick replacement is needed, segmented gaskets can be installed without removing the entire shroud assembly. - Customized Gaskets
Some steel plants use gaskets with bolt holes, slots, or special notches designed to fit unique ladle shroud manipulators or clamps.
Custom-designed ladle shroud gaskets ensure compatibility, faster installation, and better sealing performance for each plant’s casting system.
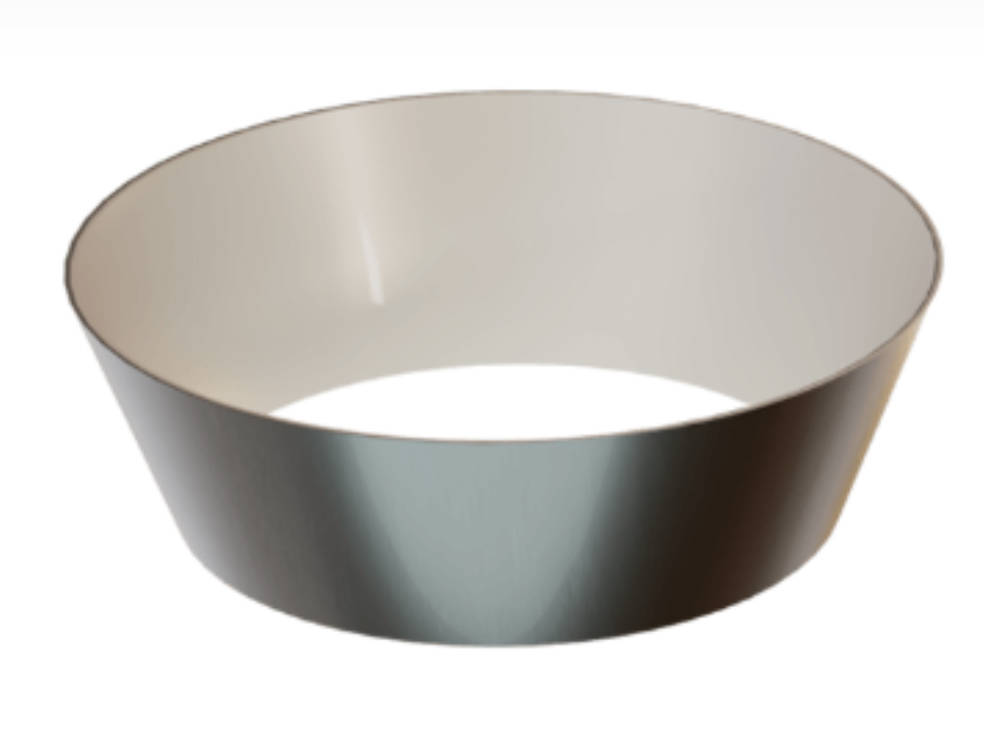

4. How to Fix or Install the Ladle Shroud Gasket
Correct installation of the ladle shroud gasket ensures stable performance and prevents steel leakage. Below is a step-by-step guide commonly used in steel plants:
- Surface Preparation
Clean both the ladle nozzle surface and the shroud head. Remove dust, slag, or metal splash to ensure proper contact. - Positioning the Gasket
Place the gasket centrally on the shroud’s upper flange. Some operators use small amounts of high-temperature adhesive or clips to keep it in place. - Aligning the Shroud
Use the ladle shroud manipulator or guiding arm to position the shroud accurately under the ladle nozzle. Proper alignment prevents gasket displacement. - Compression and Sealing
Gently press the shroud upward to compress the gasket uniformly. Avoid excessive force that could damage the gasket or deform the shroud. - Inspection Before Casting
Visually check the gasket seal around the connection. Ensure there are no visible gaps or misalignments.
Following these steps helps guarantee a safe, airtight, and reliable joint between the ladle and shroud, preventing steel leakage and oxidation.
5. Production Period and Process of Ladle Shroud Gaskets
The production period for ladle shroud gaskets depends on material selection, order volume, and customization requirements.
- Standard gaskets: 3–7 days delivery
- Custom designs: 7–15 days delivery
Typical Production Process:
- Material Cutting
Raw refractory sheets or fiber boards are precisely cut using CNC machines or die-cut molds to achieve consistent size and shape. - Drying and Heat Treatment
Some gaskets are heat-treated to remove moisture and enhance dimensional stability. - Inspection and Quality Control
Each gasket is checked for thickness, density, and flatness to ensure a perfect fit during installation. - Packaging and Storage
Finished gaskets are packed in moisture-proof boxes or cartons to prevent damage during shipping and storage.
High-quality ladle shroud gasket manufacturers maintain tight tolerances, consistent density, and clean-cut edges, ensuring reliable sealing in high-temperature casting operations.

6. Importance of Choosing a Reliable Gasket Supplier
Selecting the right ladle shroud gasket supplier ensures stable casting performance and safety. A good supplier offers:
- Material traceability and test certificates
- Dimensional accuracy and customization options
- Fast delivery and technical support
- Compatibility with various ladle shroud types
For steel plants, using high-quality ladle shroud gaskets reduces downtime, improves steel cleanliness, and extends the service life of ladle refractories.
Conclusion
The ladle shroud gasket is a small but essential component in continuous casting. Made from advanced refractory and fiber materials, it provides excellent sealing, heat resistance, and mechanical protection at the ladle-shroud interface.
By understanding the materials, functions, shapes, installation procedures, and production process of ladle shroud gaskets, operators can ensure safe and efficient steelmaking operations. A properly designed and installed gasket not only protects the ladle and shroud but also enhances steel quality and casting reliability.