1. Introduction
In modern steelmaking, precise control of molten steel flow is essential for process stability, safety, and product quality. From tapping steel out of a ladle to transferring it through the tundish and into the mold during continuous casting, flow control systems play a decisive role. One of the most widely used and robust flow control devices in secondary metallurgy and continuous casting is the slide gate system, whose core functional components are the slide gate plates.
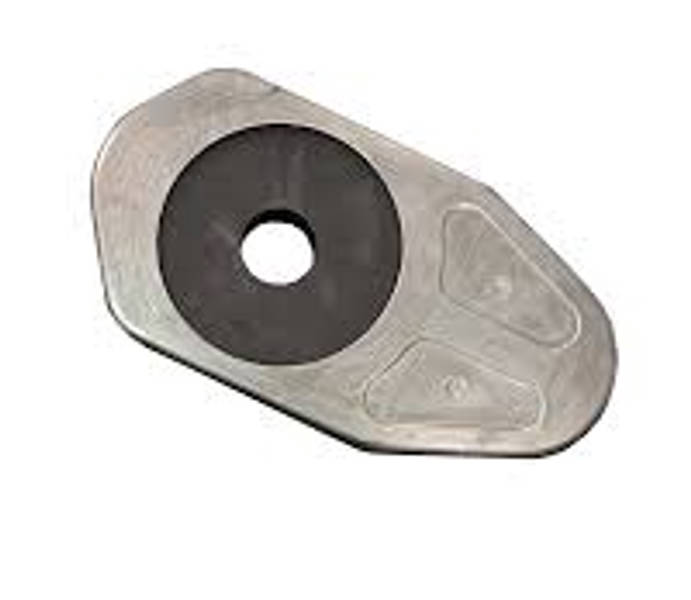

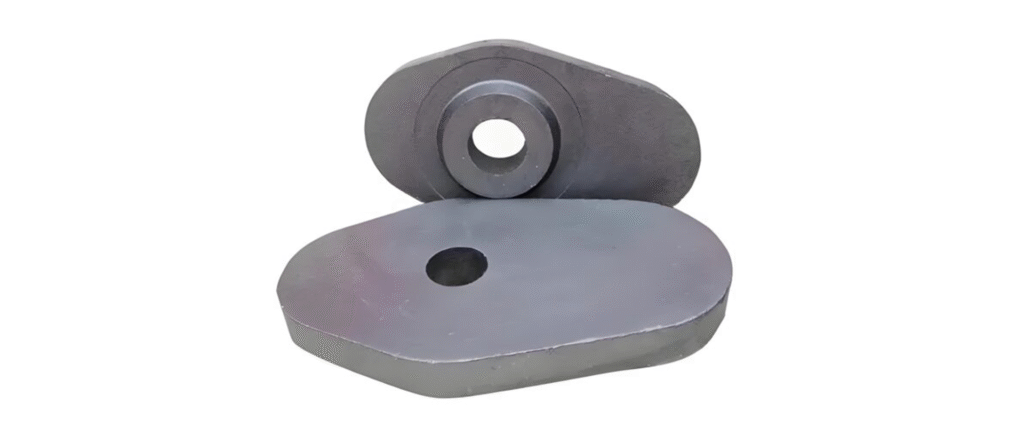
Slide gate plates are refractory plates installed at the bottom of ladles and tundishes to regulate, throttle, or completely shut off the flow of molten steel. For engineering students studying metallurgical engineering, materials science, or mechanical engineering with a focus on steel production, understanding the slide gate plate is fundamental. This article provides a comprehensive explanation of what a slide gate plate is, how it works, its materials, design features, advantages, limitations, and how it compares with other flow control systems such as stopper rods.
2. What Is a Slide Gate Plate?
A slide gate plate is a flat refractory plate with a precisely machined hole (or bore) that forms part of a sliding valve system installed at the bottom of a ladle or tundish. Typically, a slide gate system consists of:
- An upper (fixed) plate
- A lower (moving) plate
- Sometimes a middle plate (in three-plate systems)
By sliding one plate relative to another, the alignment of their internal bores changes. When the holes are aligned, molten steel flows freely; when they are misaligned, the flow rate is reduced or completely stopped.
3. Role of Slide Gate Plates in Steelmaking
3.1 Flow Control in Ladle Metallurgy
In ladle metallurgy, slide gate plates control the discharge of molten steel during:
- Tapping to tundish
- Ladle-to-ladle transfer
- Emergency shut-off situations
Precise control prevents excessive turbulence, slag entrainment, and uncontrolled steel flow.
3.2 Flow Regulation in Tundish Operations
Slide gate plates are also used in tundishes to regulate steel flow to the mold. In some casting machines, they work in combination with stopper rods or sub-entry shrouds.
3.3 Safety and Emergency Control
One of the most important functions of slide gate plates is rapid shut-off. In case of breakout, nozzle failure, or casting instability, slide gates can quickly stop steel flow, preventing accidents and equipment damage.
4. Structure and Components of a Slide Gate Plate System
4.1 Upper Plate (Fixed Plate)
- Installed directly above the nozzle
- Remains stationary during operation
- Exposed to continuous thermal and chemical attack
4.2 Lower Plate (Sliding Plate)
- Moves horizontally to open or close the flow path
- Experiences significant mechanical wear and friction
4.3 Middle Plate (Optional)
- Used in three-plate systems
- Improves sealing and wear distribution
- Allows longer service life
4.4 Steel Casing and Frame
The refractory plates are encased in steel frames to provide mechanical strength and allow integration with the slide gate mechanism.
5. Working Principle of the Slide Gate Plate

The working principle is based on controlled alignment of flow channels:
- When the holes in the upper and lower plates are fully aligned, molten steel flows through under ferrostatic pressure.
- Partial alignment reduces the effective flow area, throttling the flow.
- Complete misalignment blocks the flow entirely.
The system is actuated mechanically or hydraulically, allowing precise control even under extreme temperatures (>1600 °C).
6. Materials Used for Slide Gate Plates
Slide gate plates must withstand:
- High temperatures
- Chemical corrosion from molten steel and slag
- Mechanical abrasion
- Thermal shock
Common Materials:
- Alumina (Al₂O₃)
- Alumina–Carbon (Al₂O₃–C)
- Zirconia-containing composites
- Spinel-based refractories
Table 1: Typical Materials Used in Slide Gate Plates
| Material Type | Key Properties | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| High-purity Al₂O₃ | High refractoriness, good corrosion resistance | Carbon steels |
| Al₂O₃–C | Excellent thermal shock resistance, low wettability | Continuous casting |
| ZrO₂-containing | Superior erosion resistance | High-speed casting |
| Spinel (MgAl₂O₄) | Good slag resistance, structural stability | Special steel grades |
7. Design Considerations for Slide Gate Plates

7.1 Bore Geometry
The bore shape (cylindrical, conical, or trumpet-shaped) affects flow stability and erosion patterns.
7.2 Surface Finish
A smooth plate surface improves sealing and reduces friction during sliding.
7.3 Plate Thickness
Thicker plates offer longer life but increase thermal stress; an optimal balance is required.
8. Advantages of Slide Gate Plate Systems
- Reliable Shut-Off Capability
- High Mechanical Strength
- Suitable for Long Casting Sequences
- Compatibility with Automation
- Reduced Operator Exposure
Compared to other systems, slide gate plates are particularly robust under harsh steelmaking conditions.
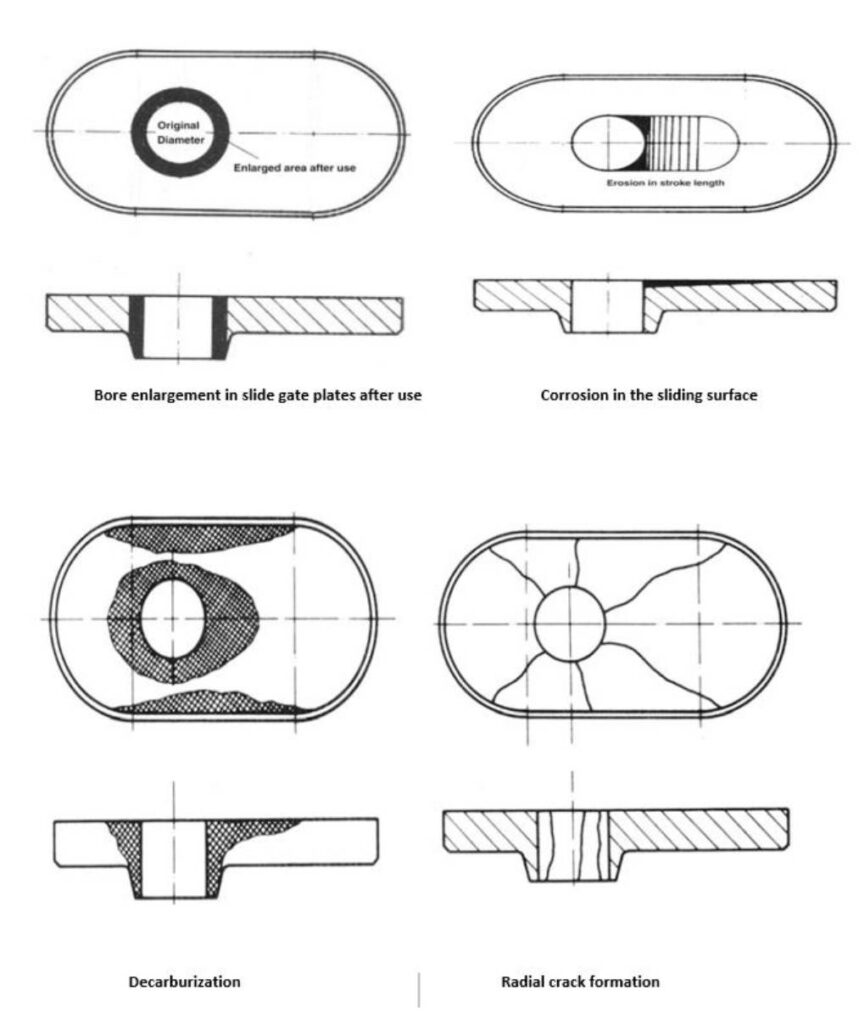
9. Common Failure Modes of Slide Gate Plates
9.1 Erosion and Corrosion
Prolonged exposure to molten steel causes gradual material loss, especially around the bore.
9.2 Thermal Shock Cracking
Rapid heating during ladle opening can induce cracks.
9.3 Plate Jamming
Steel penetration or slag infiltration between plates can prevent smooth sliding.
9.4 Leakage
Poor sealing or surface wear can lead to steel leakage, posing serious safety risks.
10. Comparison with Stopper Rod Systems
Table 2: Slide Gate Plate vs. Stopper Rod
| Aspect | Slide Gate Plate | Stopper Rod |
|---|---|---|
| Flow Control | Stepwise | Very precise |
| Shut-Off Reliability | Excellent | Good |
| Mechanical Complexity | Higher | Lower |
| Maintenance | Plate replacement | Rod alignment |
| Preferred Application | Ladle operations | Tundish operations |
Both systems are often used together in modern steel plants.
11. Importance for Engineering Students
For engineering students, slide gate plates represent a real-world application of:
- Refractory materials engineering
- Fluid mechanics
- High-temperature mechanics
- Process control in metallurgical systems
Understanding their design and operation bridges theoretical knowledge and industrial practice.
12. Recent Developments and Trends
Modern slide gate plates now incorporate:
- CFD-optimized bore designs
- Improved anti-oxidation additives
- Longer-life composite materials
- Integration with intelligent casting systems
These advances support higher productivity and cleaner steel.
13. Conclusion
The slide gate plate is a cornerstone component of modern steelmaking operations. By enabling safe, reliable, and precise control of molten steel flow, it directly influences casting stability, steel cleanliness, and operational safety. For engineering students, mastering the principles behind slide gate plates provides essential insight into how materials science, mechanical engineering, and metallurgical process control converge in industrial steel production.